Page 37 - JCAU-7-3
P. 37
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Natural ventilation in courtyard dwellings
Appendix
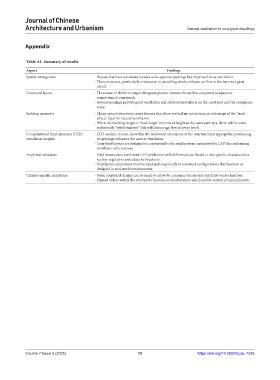
Table A1. Summary of results
Aspect Findings
Spatial arrangement - Houses that have windward facades with opposite openings had improved cross ventilation.
- These measures, particularly orientation to prevailing winds, enhance airflow in the barn to a great
extent.
Courtyard layout - The nature of the form: larger elongated planets increase the airflow compared to square or
round-shaped courtyards.
- Several openings provide good ventilation and alleviate heat effects on the courtyard and the contiguous
areas.
Building geometry - Closer spaced structures create fissures that allow vertical air circulation, an advantage of the “stack
effect,” ideal for natural ventilation.
- When the building height is much larger in terms of height to the courtyard area, there will be some
unfavorable “wind shadows” that will discourage flow at lower levels.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) - CFD models, in turn, show that the windward orientation of the courtyard and appropriate positioning
simulation insights of openings enhances the natural ventilation.
- Courtyard layouts are designed to correspond to the wind pattern anticipated by CFD thus enhancing
ventilation effectiveness.
Empirical validation - Field observation confirmed CFD prediction with differences attributed to site-specific characteristics
such as vegetation and adjacent structures.
- Ventilation calculations must be validated empirically to construct configurations that function as
designed in real-world environments.
Climate-specific adaptation - Some courtyard designs can be made to allow for a summer breeze and restricted winter heat loss.
- Planted orders within the courtyards function as windbreakers which enable control of microclimates.
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2025) 19 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.7226