Page 13 - JCBP-1-1
P. 13
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Brain MRI alterations in MDD
early in treatment, suggesting that drug treatment alters the keywords of the search were limited. Third, although
the relevant brain networks and activation status of brain exclusion criteria have been set for the retrieved literature,
regions. If a brain region is activated during task execution, comedication other than antidepressants was not restricted.
differences in individual activation levels in that region Fourth, the results of MRI spectroscopy were not included
may lead to differences in individual behavior and any in the study.
related response to medication treatment. Task-state fMRI
may provide insight into the neural changes early in drug 6. Current limitations of MRI research in
treatment. Further research is needed on the reliability of MDD and future perspectives
retesting the activation of task-state fMRI regions. A growing number of studies have examined structural and
5. Limitations of the review fMRI -derived biomarkers of response to drug treatment
of MDD and showed multiple alterations; however, the
This narrative review has some limitations. Firstly, only results lack sufficient replicability and discriminatory
two databases were searched in our study, and relative power. We summarized the research findings supported
studies before 2000 were not included, which resulted in by moderate evidence, mainly focusing on the changes
the incomplete inclusion of literature. Second, no blind in hippocampal volume, amygdala, and ACC activation
screening was conducted by independent reviewers, and (Table 1) [19,20,38,41-47,50,51] . Most studies observed that
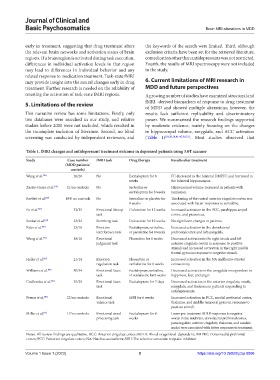
Table 1. fMRI changes and antidepressant treatment outcome in depressed patients using 3.0T scanner
Study Case number fMRI task Drug therapy Results after treatment
(MDD patients/
controls)
Wang et al. [38] 20/20 No Escitalopram for 8 FC decreased in the bilateral DMPFC and increased in
weeks the bilateral hippocampus.
Zarate-Garza et al. [19] 21/no controls No Sertraline or Hippocampal volume increased in patients with
escitalopram for 8 weeks remission.
Bartlett et al. [20] 184/ no controls No Sertraline or placebo for Thickening of the rostral anterior cingulate cortex was
8 weeks associated with better responses to sertraline.
Fu et al. [41] 32/25 Emotional Stroop Duloxetine for 12 weeks Increased activation in the PCC, parahippocampal
task cortex, and precuneus.
Sankar et al. [42] 23/22 Sternberg task Duloxetine for 12 weeks No significant changes in patients.
Fales et al. [43] 23/18 Emotion Escitalopram, sertraline, Increased activation in the dorsolateral
interference task or paroxetine for 8 weeks prefrontalcortex and left amygdala.
Wang et al. [44] 18/18 Emotional Fluoxetine for 8 weeks Decreased activationin the right insula and left
judgment task anterior cingulate cortex in response to positive
stimuli and increased activation in the right middle
frontal gyrus in response to negative stimuli.
Heller et al. [45] 21/14 Emotion Fluoxetine or Increased activation in the NA andfronto-striatal
regulation task venlafaxine for 8 weeks connectivity.
Williams et al. [46] 80/34 Emotional faces Escitalopram, sertraline, Decreased activation in the amygdala inresponders to
task or venlafaxine for 8 weeks happiness, fear, and anger.
Godlewska et al. [47] 35/29 Emotional faces Escitalopram for 7 days Decreased activation in the anterior cingulate, insula,
task amygdala, and thalamus in patients responding to
antidepressants.
Preuss et al. [50] 22/no controls Emotional SSRI for 6 weeks Increased activation in PCC, medial prefrontal cortex,
valence task thalamus, and middle temporal gyrus in response to
positive stimuli.
Miller et al. [51] 17/no controls Emotional word Escitalopram for 8 Lower pre-treatment BOLD responses to negative
processing task weeks words in the midbrain, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex,
paracingulate, anterior cingulate, thalamus, and caudate
nuclei were associated with better responses to treatment.
Notes: All review findings are qualitative. ACC: Anterior cingulate cortex; BOLD: Blood oxygenlevel-dependent; DMPFC: Dorsomedial prefrontal
cortex; PCC: Posterior cingulate cortex; NA: Nucleus accumbent; SSRI: The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.0896