Page 49 - JCBP-1-1
P. 49
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Emotional exhaustion and work–family conflict in physicians
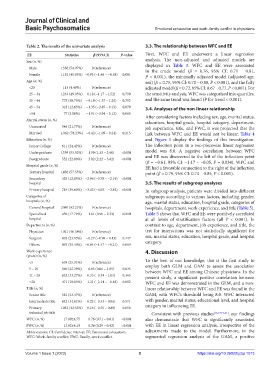
Table 2. The results of the univariate analysis 3.3. The relationship between WFC and EE
EE Statistics β (95%CI) P‑value First, WFC and EE underwent a linear regression
Sex (n, %) analysis. The non-adjusted and adjusted models are
Male 1356 (54.07%) 0 (reference) displayed in Table 3. WFC and EE were associated
in the crude model (β = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.71 – 0.81,
Female 1152 (45.93%) −0.93 (−1.48 – −0.38) 0.001 P < 0.001), the minimally adjusted model (adjusted age,
Age (n, %) sex) (β = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.70 – 0.80, P < 0.001), and the fully
<25 113 (4.49%) 0 (reference) adjusted model (β = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.67 – 0.77, P < 0.001). For
25 – 34 1233 (49.05%) 0.18 (−1.17 – 1.52) 0.799 the sensitivity analysis, WFC was categorized into quartiles,
35 – 44 773 (30.75%) −0.19 (−1.57 – 1.20) 0.792 and the same trend was found (P for trend < 0.001).
45 – 54 318 (12.65%) −1.35 (−2.85 – 0.15) 0.079 3.4. Analyses of the non-linear relationship
>54 77 (3.06%) −1.91 (−3.94 – 0.12) 0.065
Marital status (n, %) After considering factors including sex, age, marital status,
education, hospital grade, hospital category, department,
Unmarried 546 (21.77%) 0 (reference) job experience, title, and FWC, it was projected that the
Married 1,962 (78.23%) −0.42 (−1.09 – 0.24) 0.215 link between WFC and EE would not be linear. Table 4
Education (n, %) and Figure 1 display the findings of this investigation.
Junior College 611 (24.42%) 0 (reference) The inflection point in a two-piecewise linear regression
Undergraduate 1339 (53.52%) 1.99 (1.33 – 2.66) <0.001 model was 8.0. A negative correlation between WFC
Postgraduate 552 (22.06%) 3.02 (2.22 – 3.82) <0.001 and EE was discovered to the left of the inflection point
(β = −0.61, 95% CI: −1.17 – −0.05, P = 0.034). WFC and
Hospital grade (n, %) EE had a favorable connection to the right of the inflection
Tertiary hospital 1456 (57.55%) 0 (reference) point (β = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.74 – 0.85, P < 0.001).
Secondary 325 (12.85%) −2.96 (−3.78 – −2.14) <0.001
hospital 3.5. The results of subgroup analyses
Primary hospital 749 (29.60%) −3.42 (−4.03 – −2.82) <0.001 In subgroup analysis, patients were divided into different
Categories of subgroups according to various factors, including gender,
hospitals (n, %) age, marital status, education, hospital grade, categories of
General hospital 2080 (82.21%) 0 (reference) hospitals, department, work experience, and title (Table 5).
Specialized 450 (17.79%) 1.61 (0.90 – 2.33) <0.001 Table 5 shows that WFC and EE were positively correlated
hospital at all levels of stratification factors (all P < 0.001). In
Department (n, %) contrast to age, department, job experience, and title, the
Physician 1021 (40.58%) 0 (reference) test for interactions was not statistically significant for
Surgeon 602 (23.93%) −0.27 (−0.98 – 0.43) 0.447 sex, marital status, education, hospital grade, and hospital
Others 893 (35.49%) −0.84 (−1.47 – −0.21) 0.009 category.
Work experience 4. Discussion
(years) (n, %)
<5 638 (25.51%) 0 (reference) To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to
5 – 10 560 (22.39%) 0.85 (0.06 – 1.65) 0.035 employ both GLM and GAM to assess the association
between WFC and EE among Chinese physicians. In the
11 – 20 832 (33.27%) 0.33 (−0.39 – 1.05) 0.365 present study, a significant positive correlation between
>20 471 (18.83%) −1.31 (−2.14 – −0.48) 0.002 WFC and EE was demonstrated in the GLM, and a non-
Title (n, %) linear relationship between WFC and EE was found in the
Senior title 581 (23.47%) 0 (reference) GAM, with WFC’s threshold being 8.0. WFC interacted
Intermediate title 842 (34.01%) 0.22 (−0.53 – 0.96) 0.571 with gender, marital status, educational level, and hospital
Primary 1053 (42.53%) 0.16 (−0.55 – 0.88) 0.656 category in influencing EE.
technical job title Consistent with previous studies [16,17,19-21] , our findings
WFC (n, %) 17.09±4.75 0.76 (0.71 – 0.81) <0.001 also demonstrate that WFC is significantly associated
FWC (n, %) 12.02±4.19 0.36 (0.29 – 0.42) <0.001 with EE in linear regression analysis, irrespective of the
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; EE: Emotional exhaustion; adjustments made to the model. Furthermore, in the
WFC: Work–family conflict; FWC: Family–work conflict. segmented regression analysis of the GAM, a positive
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.1013