Page 62 - JCBP-1-1
P. 62
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Psychometric analysis of the mass shootings worry inventory
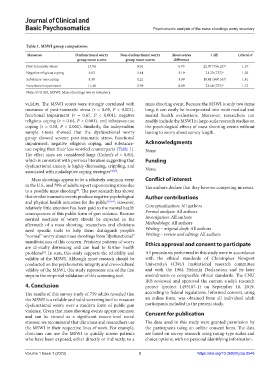
Table 1. MSWI group comparisons
Measures Dysfunctional worry Non‑dysfunctional worry Mean scores t (df) Cohen’s d
group mean scores group mean scores difference
Post-traumatic stress 15.94 9.01 6.93 22.07 (756.23) a 1.57
Negative religious coping 4.63 1.44 3.19 21.20 (757) a 1.56
Substance-use coping 4.30 1.21 3.09 18.41 (560.53) a 1.41
Functional impairment 11.48 3.39 8.09 23.44 (757) a 1.72
a
Note: P<0.001, MSWI: Mass shootings worry inventory.
validity. The MSWI scores were strongly correlated with mass shooting event. Because the MSWI is only two items
measures of post-traumatic stress (r = 0.69, P < 0.001), long, it can easily be incorporated into most medical and
functional impairment (r = 0.67, P < 0.001), negative mental health evaluations. Moreover, researchers can
religious coping (r = 0.64, P < 0.001), and substance-use readily include the MSWI in large-scale research studies on
coping (r = 0.58, P < 0.001). Similarly, the independent the psychological effects of mass shooting events without
sample t-tests showed that the dysfunctional worry having to worry about survey length.
group showed severer post-traumatic stress, functional
impairment, negative religious coping, and substance- Acknowledgments
use coping than their less worried counterparts (Table 1). None.
The effect sizes are considered large (Cohen’s d > 0.80),
which is consistent with previous literature suggesting that Funding
dysfunctional anxiety is highly distressing, crippling, and
associated with maladaptive coping strategies [4,8,9] . None.
Mass shootings appear to be a relatively common event Conflict of interest
in the U.S., and 79% of adults report experiencing stress due The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
to a possible mass shooting . The past research has shown
[6]
that similar traumatic events produce negative psychological Author contributions
and physical health outcomes for the public [15,16] . However,
relatively little attention has been paid to the mental health Conceptualization: All authors
consequences of this public form of gun violence. Because Formal analysis: All authors
normal reactions of worry should be expected in the Investigation: All authors
aftermath of a mass shooting, researchers and clinicians Methodology: All authors
need specific tools to help them distinguish people’s Writing – original draft: All authors
“normal” worry about mass shootings from “dysfunctional” Writing – review and editing: All authors
manifestations of this concern. Persistent patterns of worry Ethics approval and consent to participate
are clinically distressing and can lead to further health
problems . In sum, this study supports the reliability and All procedures performed in this study were in accordance
[6]
validity of the MSWI. Although more research should be with the ethical standards of Christopher Newport
conducted on the psychometric integrity and cross-cultural University’s (CNU) institutional research committee
validity of the MSWI, this study represents one of the first and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later
steps in the empirical validation of this screening tool. amendments or comparable ethical standards. The CNU
IRB reviewed and approved the current study’s research
4. Conclusion project (project 1493187-1) on September 18, 2019,
The results of this survey study of 759 adults revealed that according to federal regulations. Informed consent, using
the MSWI is a reliable and valid screening tool to measure an online form, was obtained from all individual adult
dysfunctional worry over a modern form of public gun participants included in the present study.
violence. Given that mass shooting events appear common Consent for publication
and can be viewed as a significant macro-level social
stressor, we recommend that clinicians and researchers use The data used in this study were granted permission by
the MSWI in their respective lines of work. For example, the participants using an online consent form. The data
clinicians can use the MSWI to quickly screen patients are based on survey research using rating-type scales and
who have been exposed, either directly or indirectly, to a choice options, with no personal identifying information.
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcbp.0546