Page 76 - JCBP-2-3
P. 76
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics HD-tDCS on pain in SSD-P
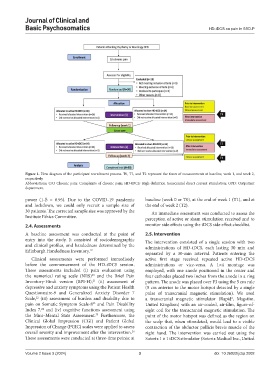
Figure 1. Flow diagram of the participant recruitment process. T0, T1, and T2 represent the times of measurements at baseline, week 1, and week 2,
respectively
Abbreviations: C/O Chronic pain: Complaints of chronic pain; HD-tDCS: High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation; OPD: Outpatient
department.
power (1-β = 0.95). Due to the COVID-19 pandemic baseline (week 0 or T0), at the end of week 1 (T1), and at
and lockdown, we could only recruit a sample size of the end of week 2 (T2).
30 patients. The corrected sample size was approved by the An immediate assessment was conducted to assess the
Institute Ethics Committee. perception of active or sham stimulation received and to
2.4. Assessments monitor side effects using the tDCS side effect checklist.
A baseline assessment was conducted at the point of 2.5. Intervention
entry into the study. It consisted of sociodemographic The intervention consisted of a single session with two
and clinical profiles, and handedness determined by the administrations of HD-tDCS, each lasting 30 min and
Edinburgh Handedness Inventory. 19 separated by a 30-min interval. Patients entering the
Clinical assessments were performed immediately active first stage received repeated active HD-tDCS
before the commencement of the HD-tDCS session. administrations or vice-versa. A 1×4 montage was
These assessments included (i) pain evaluation using employed, with one anode positioned in the center and
the numerical rating scale (NRS) and the Brief Pain four cathodes placed two inches from the anode in a ring
20
Inventory-Hindi version (BPI-H), (ii) assessment of pattern. The anode was placed over F3 using the 5 cm rule
21
depressive and anxiety symptoms using the Patient Health (5 cm anterior to the motor hotspot detected by a single
Questionnaire-9 and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 pulse of transcranial magnetic stimulation). We used
Scale, (iii) assessment of burden and disability due to a transcranial magnetic stimulator (Rapid , Magstim,
22
2
pain on Somatic Symptom Scale-8 and Pain Disability United Kingdom) with an air-cooled, air-film, figure-of-
23
Index 7, and (iv) cognitive functions assessment using eight coil for the transcranial magnetic stimulation. The
24
the Mini–Mental State Assessment. Furthermore, the point of the motor hotspot was defined as the region on
25
Clinical Global Impression (CGI) and Patient Global the scalp that, when stimulated, would lead to a visible
Impression of Change (PGIC) scales were applied to assess contraction of the abductor pollicis brevis muscle of the
overall severity and improvement after the intervention. right hand. The intervention was carried out using the
26
These assessments were conducted at three-time points: at Soterix 1 × 1 tDCS stimulator (Soterix Medical Inc., United
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.2002