Page 46 - JCBP-3-2
P. 46
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Mental health status of Chinese college students in the post-epidemic period
severe
Since the restrictions have been relaxed, do you worry about highly vulnerable families and relatives being infected? moderate 21% 29% 39%
light
No
12%
Series1
11%
other
What do you think is the health barrier to mental health? Lack of resource information 11% 12% 31% 35%
Economics
Social discrimination
Limited resources
severe
Were you afraid of taking public transport after the COVID-19 restrictions were relaxed? moderate 5% 13% 34% 48%
light
No
severe
Did you worry about being infected after the restrictions were relaxed? moderate 8% 23% 27% 42%
light
No
severe
Did you pay more attention to the treatment methods for COVID-19 after the restrictions were relaxed? moderate 10% 16% 33% 41%
light
No
increase
Did your overall pressure increase/decre ase or remain unchanged after the easing of the COVID-19 restrictions? remain unchanged 12% 40% 48%
reduce
Could you fully cope with the pressure after the restrictions were eased? perhaps 10% 43% 47%
No
Yes
No
Do you think other students feel pressure/ anxiety because of the easing of the restrictio ns? Yes 43% 58%
severe 2%
Do you lack knowledge of COVID-19 transmission or infection? moderate 12% 45%
light
No 6% 41%
severe
After the COVID- 19 pandemic restrictions were relaxed, did you reduce your interactions with others? moderate 18% 36% 39%
light
No
severe
Was it more difficult to purchase COVID- 19 prevention materials after the restrictions were eased? moderate 21% 29%
30%
light
No
SRSS Sleep disorders 20% 28% 72%
normal
severe 2%
Moderate and severe 6%
PHQ-9 moderate 12%
light 35%
normal 46%
severe 17%
PSS-10 moderate 54%
normal 30%
severe 3%
GAD-7 moderate 6% 24%
light
normal 67%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80%
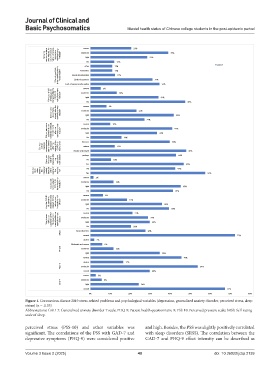
Figure 1. Coronavirus disease 2019 stress-related problems and psychological variables (depression, generalized anxiety disorder, perceived stress, sleep
status) (n = 1105)
Abbreviations: GAD-7: Generalized anxiety disorder-7 scale; PHQ-9: Patient health questionnaire-9; PSS-10: Perceived pressure scale; SRSS: Self-rating
scale of sleep.
perceived stress (PSS-10) and other variables was and high. Besides, the PSS was slightly positively correlated
significant. The correlations of the PSS with GAD-7 and with sleep disorders (SRSS). The correlation between the
depressive symptoms (PHQ-9) were considered positive GAD-7 and PHQ-9 effect intensity can be described as
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 40 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.2139