Page 53 - JCBP-3-4
P. 53
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Emotion and blood pressure variability
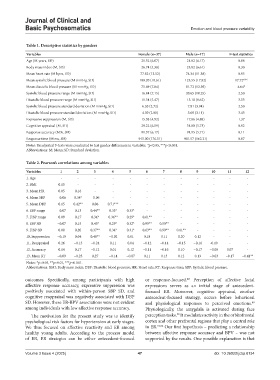
Table 1. Descriptive statistics by genders
Variables Female (n=37) Male (n=17) F‑test statistics
Age (M years, SD) 21.32 (6.07) 21.82 (6.17) 0.08
Body mass index (M, SD) 26.74 (5.30) 25.82 (6.61) 0.30
Mean heart rate (M bpm, SD) 77.82 (12.52) 74.34 (11.38) 0.95
Mean systolic blood pressure (M mmHg, SD) 109.20 (10.61) 125.55 (17.82) 17.72***
Mean diastolic blood pressure (M mmHg, SD) 75.69 (7.84) 81.72 (12.59) 4.64*
Systolic blood pressure range (M mmHg, SD) 16.84 (7.15) 20.65 (10.25) 2.50
Diastolic blood pressure range (M mmHg, SD) 11.54 (5.47) 15.18 (8.62) 3.53
Systolic blood pressure standard deviation (M mmHg, SD) 6.35 (2.72) 7.81 (3.94) 2.50
Diastolic blood pressure standard deviation (M mmHg, SD) 4.39 (2.00) 5.69 (3.11) 3.43
Expressive suppression (M, SD) 15.38 (4.92) 17.06 (4.88) 1.37
Cognitive appraisal (M, SD) 29.22 (6.59) 31.00 (5.73) 0.92
Response accuracy (M%, SD) 91.37 (6.17) 91.95 (5.71) 0.11
Response time (M ms, SD) 915.00 (176.51) 901.57 (162.21) 0.07
Notes: Unadjusted F-tests were conducted to test gender differences in variables. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: M: Mean; SD: Standard deviation.
Table 2. Pearson’s correlations among variables
Variables 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
1. Age - - - - - - - - - - - -
2. BMI 0.15 - - - - - - - - - - -
3. Mean HR 0.05 0.16 - - - - - - - - - -
4. Mean SBP −0.06 0.34* −0.06 - - - - - - - - -
5. Mean DBP 0.15 0.42** 0.06 0.71*** - - - - - - - -
6. SBP range −0.07 0.13 0.44** 0.33* 0.33* - - - - - - -
7. DBP range 0.09 0.17 0.34* 0.36** 0.29* 0.61** - - - - - -
8. SBP SD −0.07 0.15 0.45* 0.29* 0.32* 0.99** 0.59** - - - - -
9. DBP SD 0.08 0.20 0.37** 0.34* 0.31* 0.63** 0.99** 0.61** - - - -
10. Suppression −0.19 0.04 0.40** −0.02 0.01 0.18 0.11 0.20 0.12 - - -
11. Reappraisal 0.26 −0.13 −0.24 0.11 0.04 −0.12 −0.14 −0.15 −0.16 -0.19 - -
12. Accuracy 0.14 0.17 −0.12 0.01 0.12 −0.11 −0.16 0.10 −0.17 −0.05 0.07 -
13. Mean RT −0.09 −0.25 0.27 −0.14 −0.07 0.11 0.13 0.12 0.13 −0.03 −0.17 −0.41**
Notes: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; HR: Heart rate; RT: Response time; SBP: Systolic blood pressure.
outcomes. Specifically, among participants with high or response-focused. Perception of affective facial
48
affective response accuracy, expressive suppression was expressions serves as an initial stage of antecedent-
positively associated with within-person SBP SD, and focused ER. Moreover, cognitive appraisal, another
cognitive reappraisal was negatively associated with DBP antecedent-focused strategy, occurs before behavioral
SD. However, these ER-BPV associations were not evident and physiological responses to perceived emotions.
49
among individuals with low affective response accuracy. Physiologically, the amygdala is activated during face
50
The motivation for the present study was to identify perception tasks. It modulates activity in the orbitofrontal
psychological risk factors for hypertension at early stages. cortex and other prefrontal regions that play a central role
We thus focused on affective reactivity and ER among in ER. 51,52 Our first hypothesis – predicting a relationship
healthy young adults. According to the process model between affective response accuracy and BPV – was not
of ER, ER strategies can be either antecedent-focused supported by the results. One possible explanation is that
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2025) 47 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.8134