Page 39 - JCTR-11-3
P. 39
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Immunogenicity and safety of flu vaccines
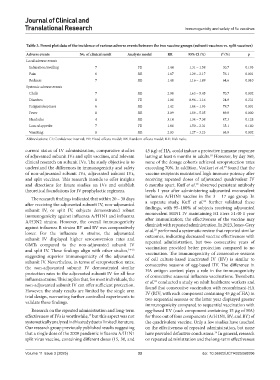
Table 3. Forest plot data of the incidence of various adverse events between the two vaccine groups (subunit vaccines vs. split vaccines)
Adverse events No. of clinical result Analysis model RR 95% Cl (%) I (%) p
2
Local adverse events
Induration/swelling 7 FE 1.44 1.31 – 1.58 30.7 0.193
Pain 6 RE 1.67 1.29 – 2.17 76.1 0.001
Redness 7 RE 1.48 1.16 – 1.89 64.6 0.010
Systemic adverse events
Chills 7 RE 2.98 1.63 – 5.45 70.7 0.002
Diarrhea 8 FE 1.06 0.96 – 1.16 24.8 0.231
Fatigue/sleepiness 6 RE 1.42 1.04 – 1.93 79.7 0.001
Fever 8 RE 3.09 1.89 – 5.05 89.8 0.000
Headache 4 RE 3.14 1.34 – 7.38 47.3 0.128
Loss of appetite 7 FE 1.86 1.50 – 2.31 35.1 0.160
Vomiting 8 RE 2.03 1.27 – 3.23 68.8 0.002
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; FE: Fixed-effects model; RE: Random-effects model; RR: Risk ratio.
current status of IV administration, comparative studies 45 μg) of HA, could induce a protective immune response
of adjuvanted subunit IVs and split vaccines, and relevant lasting at least 6 months in adults. However, by day 360,
18
clinical research on subunit IVs. The study objective is to none of the dosage cohorts achieved seroprotection rates
understand the differences in immunogenicity and safety exceeding 70%. In addition, Vesikari et al. found that the
19
of non-adjuvanted subunit IVs, adjuvanted subunit IVs, vaccine recipients maintained high immune potency after
and split vaccines. This research intends to offer insights receiving repeated doses of adjuvanted quadrivalent IV
and directions for future studies on IVs and establish 6 months apart. Kuff et al. observed persistent antibody
20
theoretical foundations for IV prophylactic regimens. levels 1 year after administering adjuvanted monovalent
influenza A/H1N1 vaccine in the 3 – 17 age group. In
The research findings indicated that within 20 – 30 days 21
after receiving the adjuvanted subunit IV, non-adjuvanted a separate study, Kuff et al. further validated these
subunit IV, or split IV, subjects demonstrated robust findings, with 95–100% of subjects receiving adjuvanted
immunogenicity against influenza A/H1N1 and influenza monovalent H1N1 IV maintaining HI titers ≥1:40 1 year
A/H3N2 strains. However, the overall immunogenicity after immunization; the effectiveness of the vaccine may
diminish with repeated administration. In 2023, Jones-Gray
against influenza B strains BY and BV was comparatively et al. performed a systematic review that reported similar
22
lower. For the influenza A strains, the adjuvanted outcomes, indicating decreased vaccine effectiveness with
subunit IV displayed higher seroconversion rates and
GMTs compared to the non-adjuvanted subunit IV repeated administration, but two consecutive years of
vaccination provided better protection compared to no
and split IV. These findings align with other studies, 14-16 vaccination. The immunogenicity of consecutive seasons
suggesting superior immunogenicity of the adjuvanted of cell culture-based inactivated IV (IIV) is similar to
subunit IV. Nevertheless, in terms of seroprotection rates, consecutive seasons of egg-based IIV. The difference in
the non-adjuvanted subunit IV demonstrated similar HA antigen content plays a role in the immunogenicity
protection rates to the adjuvanted subunit IV for all four of consecutive seasonal influenza vaccinations. Trombetta
influenza strains. This implies that, for most individuals, the et al. conducted a study on adult healthcare workers and
23
non-adjuvanted subunit IV can offer sufficient protection. found that consecutive vaccination with recombinant-HA
However, the study results are limited by the single arm IV (RIV; with each component containing 45 μg of HA) in
trial design, warranting further controlled experiments to two sequential seasons or the latter year displayed greater
validate these findings. immunogenicity compared to sequential vaccination with
Research on the repeated administration and long-term egg-based IIV (each component containing 15 μg of HA)
effectiveness of IVs is worthwhile, but this aspect was not for three out of four components (A/H1N1, BV, and BY) of
17
systematically analyzed in this study due to limited literature. the quadrivalent vaccine. Only a few studies have touched
Our research group previously published results suggesting on the effectiveness of repeated administration, but none
that a single dose of the 2009 pandemic influenza A/H1N1 have provided definitive conclusions. In general, research
24
split virus vaccine, containing different doses (15, 30, and on repeated administration and the long-term effectiveness
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025060006