Page 58 - JCTR-11-3
P. 58
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Telerehabilitation after stroke
such as the small number of studies directly addressing the Emmerson et al. conducted an RCT comparing
10
research question. home exercise programs for post-stroke patients using
smart technology (videos and automated reminders)
3. Results with traditional paper-based programs. Participants were
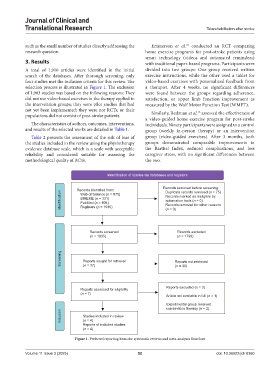
A total of 1,910 articles were identified in the initial divided into two groups: One group received written
search of the databases. After thorough screening, only exercise instructions, while the other used a tablet for
four studies met the inclusion criteria for this review. The video-based exercises with personalized feedback from
selection process is illustrated in Figure 1. The exclusion a therapist. After 4 weeks, no significant differences
of 1,903 studies was based on the following reasons: They were found between the groups regarding adherence,
did not use video-based exercises in the therapy applied to satisfaction, or upper limb function improvement as
the intervention groups; they were pilot studies that had measured by the Wolf Motor Function Test (WMFT).
not yet been implemented; they were not RCTs; or their 13
populations did not consist of post-stroke patients. Similarly, Redzuan et al. assessed the effectiveness of
a video-guided home exercise program for post-stroke
The characteristics of authors, outcomes, interventions, individuals. Ninety participants were assigned to a control
and results of the selected works are detailed in Table 1. group (weekly in-person therapy) or an intervention
Table 2 presents the assessment of the risk of bias of group (video-guided exercises). After 3 months, both
the studies included in the review using the physiotherapy groups demonstrated comparable improvements in
evidence database scale, which is a scale with acceptable the Barthel Index, reduced complications, and less
reliability and considered suitable for assessing the caregiver stress, with no significant differences between
methodological quality of RCTs. the two.
Identification of studies via databases and registers
Records removed before screening:
Records identified from: Duplicate records removed (n = 75)
Identification BIREME (n = 331) Records marked as ineligible by
Web of Science (n = 975)
automation tools (n = 0)
PubMed (n = 604)
Records removed for other reasons
Registers (n = 1910)
(n = 0)
Records screened Records excluded
(n = 1835) (n = 1798)
Screening Reports sought for retrieval Reports not retrieved
(n = 37)
(n = 30)
Reports excluded (n = 3)
Reports assessed for eligibility
(n = 7) Article not available in full (n = 1)
Experimental group received
combination therapy (n = 2)
Inclusion Studies included in review
(n = 4)
Reports of included studies
(n = 4)
Figure 1. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses flowchart
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 52 doi: 10.36922/jctr.8360