Page 69 - JCTR-11-3
P. 69
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research N-NOSE: Early cervical cancer screening
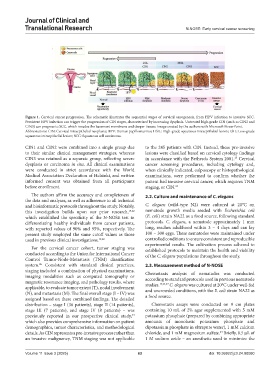
Figure 1. Cervical cancer progression. The schematic illustrates the sequential stages of cervical oncogenesis, from HPV infection to invasive SCC.
Persistent HPV infection can trigger the progression of CIN stages, characterized by increasing dysplasia. Untreated high-grade CIN (such as CIN2 and
CIN3) can progress to SCC, which invades the basement membrane and deeper tissues. Image created by the authors with Microsoft PowerPoint.
Abbreviations: CIN: Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HPV: Human papillomavirus; HSIL: High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL: Low-grade
squamous intraepithelial lesion; SCC: Squamous cell carcinoma.
CIN1 and CIN2 were combined into a single group due to the 245 patients with CIN. Instead, these pre-invasive
to their similar clinical management strategies, whereas lesions were classified based on cervical cytology findings
CIN3 was retained as a separate group, reflecting severe in accordance with the Bethesda System 2001. Cervical
25
dysplasia or carcinoma in situ. All clinical examinations cancer screening procedures, including cytology and,
were conducted in strict accordance with the World when clinically indicated, colposcopy or histopathological
Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, and written examinations, were performed to confirm whether the
informed consent was obtained from all participants patient had invasive cervical cancer, which requires TNM
before enrollment. staging, or CIN. 24
The authors affirm the accuracy and completeness of 2.2. Culture and maintenance of C. elegans
the data and analyses, as well as adherence to all technical
and bioinformatic protocols throughout the study. Notably, C. elegans (wild-type N2) were cultured at 20°C on
this investigation builds upon our prior research, 19,22 nematode growth media seeded with Escherichia coli
which established the specificity of the N-NOSE test in (E. coli) strain NA22 as a food source, following standard
differentiating healthy individuals from cancer patients, protocols. C. elegans, a nematode approximately 1 mm
with reported values of 90% and 95%, respectively. The long, reaches adulthood within 3 – 4 days and can lay
present study employed the same cutoff values as those 100 – 300 eggs. These nematodes were maintained under
used in previous clinical investigations. 19,22 controlled conditions to ensure consistent and reproducible
experimental results. The cultivation process adhered to
For the cervical cancer cohort, tumor staging was established protocols to maintain the health and viability
conducted according to the Union for International Cancer of the C. elegans populations throughout the study.
Control Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) classification
26
system. Consistent with standard clinical practices, 2.3. Measurement method of N-NOSE
staging included a combination of physical examinations, Chemotaxis analysis of nematodes was conducted
imaging modalities such as computed tomography or according to standard protocols used in previous nematode
magnetic resonance imaging, and pathology results, where studies. 19,24,27 C. elegans was cultured at 20°C under well-fed
applicable, to evaluate tumor extent (T), nodal involvement and uncrowded conditions, with the E. coli strain NA22 as
(N), and metastasis (M). The final overall stage (I – IV) was a food source.
assigned based on these combined findings. The detailed
distribution – stage I (36 patients), stage II (14 patients), Chemotaxis assays were conducted on 9 cm plates
stage III (7 patients), and stage IV (8 patients) – was containing 10 mL of 2% agar supplemented with 5 mM
previously reported in our prospective clinical study, potassium phosphate (prepared by combining appropriate
24
which also provides comprehensive information on patient amounts of monobasic potassium phosphate and
demographics, tumor characteristics, and methodological dipotassium phosphate in ultrapure water), 1 mM calcium
details. As CIN represents a pre-invasive process rather than chloride, and 1 mM magnesium sulfate. Briefly, 0.5 μL of
24
an invasive malignancy, TNM staging was not applicable 1 M sodium azide – an anesthetic used to minimize the
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 63 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00080