Page 39 - MI-2-1
P. 39
Microbes & Immunity iPSC-derived NK cell immunotherapy
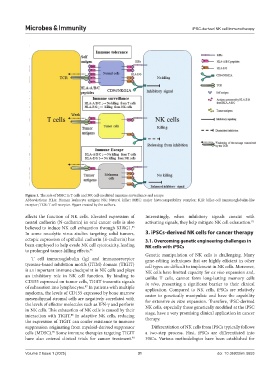
Figure 1. The role of MHC in T cells and NK cell-mediated immune surveillance and escape
Abbreviations: HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; NK: Natural killer; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; KIR: killer-cell immunoglobulin-like
receptor; TCR: T cell receptor. Figure created by the authors.
affects the function of NK cells. Elevated expression of Interestingly, when inhibitory signals coexist with
neural cadherin (N-cadherin) in oral cancer cells is also activating signals, they help mitigate NK cell exhaustion. 91
85
believed to induce NK cell exhaustion through KLRG1.
In some oncolytic virus studies targeting solid tumors, 3. iPSCs-derived NK cells for cancer therapy
ectopic expression of epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) has 3.1. Overcoming genetic engineering challenges in
been employed to help evade NK cell cytotoxicity, leading NK cells with iPSCs
to prolonged tumor-killing effects. 86
Genetic manipulation of NK cells is challenging. Many
T cell immunoglobulin (Ig) and immunoreceptor gene-editing techniques that are highly efficient in other
tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIM) domain (TIGIT) cell types are difficult to implement in NK cells. Moreover,
is an important immune checkpoint in NK cells and plays NK cells have limited capacity for ex vivo expansion and,
an inhibitory role in NK cell function. By binding to unlike T cells, cannot form long-lasting memory cells
CD155 expressed on tumor cells, TIGIT transmits signals in vivo, presenting a significant barrier to their clinical
of exhaustion into lymphocytes. In patients with multiple application. Compared to NK cells, iPSCs are relatively
87
myeloma, the levels of CD155 expressed by bone marrow easier to genetically manipulate and have the capability
mesenchymal stromal cells are negatively correlated with for extensive in vitro expansion. Therefore, iPSC-derived
the levels of effector molecules such as IFN-γ and perforin NK cells, especially those genetically modified at the iPSC
in NK cells. This exhaustion of NK cells is caused by their stage, have a very promising clinical application in cancer
interaction with TIGIT. In adaptive NK cells, reducing
88
the expression of TIGIT can confer resistance to immune therapy.
suppression originating from myeloid-derived suppressor Differentiation of NK cells from iPSCs typically follows
cells (MDSC). Some immune therapies targeting TIGIT a two-step process. First, iPSCs are differentiated into
89
have also entered clinical trials for cancer treatment. HSCs. Various methodologies have been established for
90
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 31 doi: 10.36922/mi.5653