Page 9 - MSAM-2-4
P. 9
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Emerging 3D-printed zeolitic gas adsorbents
number of their corresponding element groups . As minerals such as kaolin are regarded as the natural material
[35]
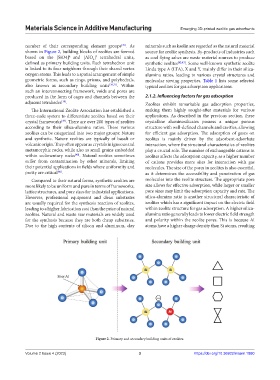
shown in Figure 2, building blocks of zeolites are formed source for zeolite synthesis. By-products of industries such
based on the [SiO4] and [AlO ] tetrahedral units, as coal flying ashes are waste material sources to produce
4-
5-
4
defined as primary building units. Each tetrahedron unit synthetic zeolites [42,43] . Some well-known synthetic zeolite
is linked to its four neighbors through their shared vertex Linda type A (LTA), X and Y, mainly differ in their silica-
oxygen atoms. This leads to a spatial arrangement of simple alumina ratios, leading to various crystal structures and
geometric forms, such as rings, prisms, and polyhedrals, molecular sieving properties. Table 1 lists some selected
also known as secondary building units [36,37] . Within typical zeolites for gas adsorption applications.
such an interconnecting framework, voids and pores are
produced in the form of cages and channels between the 2.1.2. Influencing factors for gas adsorption
adjacent tetrahedra . Zeolites exhibit remarkable gas adsorption properties,
[38]
The International Zeolite Association has established a making them highly sought-after materials for various
three-code system to differentiate zeolites based on their applications. As described in the previous section, these
crystal frameworks . There are over 200 types of zeolites crystalline aluminosilicates possess a unique porous
[39]
according to their silica-alumina ratios. These various structure with well-defined channels and cavities, allowing
zeolites can be categorized into two major groups: Nature for efficient gas adsorption. The adsorption of gases on
and synthetic. Nature zeolites are typically of basalt or zeolites is mainly driven by the adsorbent-adsorbate
volcanic origin. They often appear as crystals in igneous and interaction, where the structural characteristics of zeolites
metamorphic rocks, while also as small grains embedded play a crucial role. The number of exchangeable cations in
within sedimentary rocks . Natural zeolites sometimes zeolites affects the adsorption capacity, as a higher number
[40]
suffer from contamination by other minerals, limiting of cations provides more sites for interaction with gas
their potential applications in fields where uniformity and molecules. The size of the pores in zeolites is also essential,
purity are critical . as it determines the accessibility and penetration of gas
[41]
Compared to their natural forms, synthetic zeolites are molecules into the zeolite structure. The appropriate pore
more likely to be uniform and pure in terms of frameworks, size allows for effective adsorption, while larger or smaller
lattice structures, and pore sizes for industrial applications. pore sizes may limit the adsorption capacity and rate. The
However, professional equipment and clean substrates silica-alumina ratio is another structural characteristic of
are usually required for the synthesis reaction of zeolites, zeolites which has a significant impact on the electric field
leading to a higher fabrication cost than the price of natural within zeolite structure for gas adsorption. A higher silica-
zeolites. Natural and waste raw materials are widely used alumina ratio generally leads to lower electric field strength
for the synthesis because they are both cheap substrates. and polarity within the zeolite pores. This is because Al
Due to the high contents of silicon and aluminum, clay atoms have a higher charge density than Si atoms, resulting
Figure 2. Primary and secondary building units of zeolites.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.1880