Page 13 - MSAM-2-4
P. 13
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Emerging 3D-printed zeolitic gas adsorbents
rate and capacity. Since each 3D printing system has its two main steps: pretreatment of materials and feedstock
unique manufacturing process, feedstock materials, and final deposition through nozzles [78-80] . In 1992, Scott Crump
products, a suitable system needs to be selected for specific invented fused deposition modeling (FDM), the first type
technical requirements. Therefore, a brief introduction of extrusion-based 3D printing process . Thermoplastic
[81]
of 3D printing systems, such as photopolymerization, filaments are generally utilized for the FDM process in
extrusion, powder-based, and lamination, is given below which they are preheated to a semi-molten status. The
to provide a basic understanding of their applications for dispenser nozzle would deposit the materials onto the
zeolitic gas adsorbent manufacturing. substrate in a layer-by-layer manner . Figure 6 shows
[82]
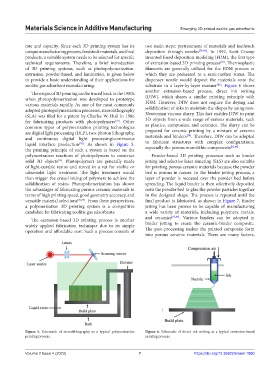
The origin of 3D printing can be traced back to the 1980s another extrusion-based process, direct ink writing
when photopolymerization was developed to prototype (DIW), which shares a similar printing principle with
various materials rapidly. As one of the most commonly FDM. However, DIW does not require the drying and
adopted photopolymerization processes, stereolithography solidification of inks to maintain the shapes by using non-
(SLA) was filed for a patent by Charles W. Hull in 1986 Newtonian viscous slurry. This fact enables DIW to print
for fabricating products with photopolymers . Other 3D objects from a wide range of various materials, such
[73]
common types of polymerization printing technologies as plastics, composites, and ceramics. The slurry can be
are digital light processing (DLP), two-photon lithography, prepared for ceramic printing by a mixture of ceramic
[78]
and continuous digital light processing/continuous materials and binders . Therefore, DIW can be adopted
liquid interface production . As shown in Figure 5, to fabricate structures with complex configurations,
[74]
[83,84]
the printing principle of such a system is based on the especially the porous monolithic components .
polymerization reactions of photopolymers to construct Powder-based 3D printing processes such as binder
solid 3D objects . Photopolymers are generally made jetting and selective laser sintering (SLS) are also suitable
[75]
of light-curable resins and stored in a vat for visible or for printing porous ceramic materials because the powder
ultraviolet light treatment. The light treatment would bed is porous in nature. In the binder jetting process, a
then trigger the cross-linking of polymers to achieve the layer of powder is recoated over the powder bed before
solidification of resins. Photopolymerization has shown spreading. The liquid binder is then selectively deposited
the advantages of fabricating porous ceramic materials in onto the powder bed to glue the powder particles together
terms of high printing speed, good geometry accuracy, and in the designed shape. The process is repeated until the
versatile material selections [76,77] . From these perspectives, final product is fabricated, as shown in Figure 7. Binder
a polymerization 3D printing system is a competitive jetting has been proven to be capable of manufacturing
candidate for fabricating zeolitic gas adsorbents. a wide variety of materials, including polymers, metals,
The extrusion-based 3D printing process is another and ceramics [85,86] . Various binders can be adopted in
widely applied fabrication technique due to its simple binder jetting to create the ceramic-binder composite.
operation and affordable cost. Such a process consists of The post-processing makes the printed composite form
into porous ceramic materials. There are many factors,
Figure 5. Schematic of stereolithography as a typical polymerization Figure 6. Schematic of direct ink writing as a typical extrusion-based
printing process. printing process.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.1880