Page 38 - TD-1-2
P. 38
Tumor Discovery Fact & challenges of immunotherapy in TNBC
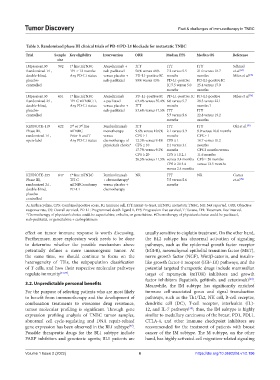
Table 3. Randomized phase III clinical trials of PD‑1/PD‑L1 blockade for metastatic TNBC
Trial Sample Key eligibility Intervention ORR Median PFS Median OS Reference
size
IMpassion130 902 1 line mTNBC Atezolizumab + ITT ITT ITT Schmid
st
Randomized 1:1, TFI ≥ 12 months nab-paclitaxel 56% versus 46% 7.2 versus 5.5 21.0 versus 18.7 et al. [69]
double-blind, Any PD-L1 status versus placebo + PD-L1-positive IC months months Miles et al. [74]
placebo- nab-paclitaxel 59% versus 43% PD-L1-positive PD-L1-positive IC
controlled IC 7.5 versus 5.0 25.4 versus 17.9
months months
IMpassion130 651 1 line mTNBC Atezolizumab PD-L1-positive IC PD-L1-positive IC PD-L1-positive Miles et al. [74]
st
Randomized 2:1, TFI C mTNBC :1, + paclitaxel 63.4% versus 55.4% 6.0 versus 5.7 28.3 versus 22.1
double-blind, Any PD-L1 status versus placebo + ITT months months I
placebo- nab-paclitaxel 53.6% versus 47.5% ITT ITT
controlled 5.7 versus 5.6 22.8 versus 19.2
months months
KEYNOTE-119 622 2 or 3 line Pembrolizumab ITT ITT ITT Oki et al. [75]
rd
nd
Phase III, mTNBC monotherapy 9.6% versus 10.6% 2.1 versus 3.3 9.9 versus 10.8 months
randomized 1:1, Prior A and T versus CPS ≥ 1 months CPS ≥ 1
open-label Any PD-L1 status chemotherapy of 12.3% versus 9.4% CPS ≥ 1 10.7 versus 10.2
physician’s choice* CPS ≥ 10 2.1 versus 3.1 months
17.7% versus 9.2% months CPS 2 months versus
CPS ≥ 20 CPS ≥ 10 2.1 11.6 months
26.3% versus 11.5% versus 3.4 months CPS ≥ 20 months
CPS ≥ 20 3.4 versus 12.5 months
versus 2.4 months
KEYNOTE-355 847 1 line mTNBC Pembrolizumab NR ITT NR Cortes
st
Phase III, TFI C + chemotherapy # 7.5 versus 5.6 et al. [76]
randomized 2:1, mTNBCrandoany versus placebo + months
double-blind, PD-L1 chemotherapy
placebo-
controlled
A: Anthracycline, CPS: Combined positive score, IC: Immune cell, ITT: Intent-to-treat, mTNBC: metastatic TNBC, NR: Not reported, ORR: Objective
response rate, OS: Overall survival, PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1, PFS: Progression-free survival, T: Taxane, TFI: Treatment-free interval.
*Chemotherapy of physician’s choice could be capecitabine, eribulin, or gemcitabine. #Chemotherapy of physician’s choice could be paclitaxel,
nab-paclitaxel, or gemcitabine + carboplatinum
effect on tumor immune response is worth discussing. usually sensitive to cisplatin treatment. On the other hand,
Furthermore, more exploratory work needs to be done the BL2 subtype has abnormal activation of signaling
to determine whether the possible mechanism above pathways, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor
potentially defines a more immunogenic tumor. At (EGFR), mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET),
the same time, we should continue to focus on the nerve growth factor (NGF), Wnt/β-catenin, and insulin-
heterogeneity of TILs, the subpopulation classification like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) pathways, and the
of T cells, and how their respective molecular pathways potential targeted therapeutic drugs include mammalian
regulate immunity [44,73] . target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors and growth
factor inhibitors (lapatinib, gefitinib, and cetuximab) .
[64]
3.2. Unpredictable personal benefits Meanwhile, the IM subtype has significantly enriched
For the purpose of selecting patients who are most likely immune cell-associated genes and signal transduction
to benefit from immunotherapy and the development of pathways, such as the Th1/Th2, NK cell, B-cell receptor,
combination treatments to overcome drug resistance, dendritic cell (DC), T-cell receptor, interleukin (IL)-
[78]
tumor molecular profiling is significant. Through gene 12, and IL-7 pathways ; thus, the IM subtype is highly
expression profiling analysis of TNBC tumor samples, similar to medullary carcinoma of the breast. PD1, PDL1,
abnormal cell cycle-regulating and DNA repair-related CTLA-4, and other immune checkpoint inhibitors are
gene expression has been observed in the BL1 subtype . recommended for the treatment of patients with breast
[77]
Possible therapeutic drugs for the BL1 subtype include cancer of the IM subtype. The M subtype, on the other
PARP inhibitors and genotoxic agents; BL1 patients are hand, has highly activated cell migration-related signaling
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.v1i2.196