Page 35 - TD-1-2
P. 35
Tumor Discovery Fact & challenges of immunotherapy in TNBC
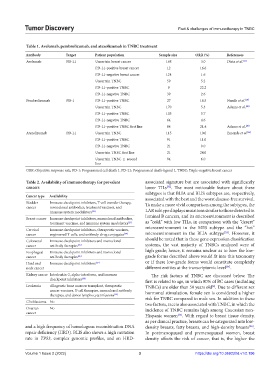
Table 1. Avelumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab in TNBC treatment
Antibody Target Patient population Sample size ORR (%) References
Avelumab PD-L1 Uncertain breast cancer 168 3.0 Dirix et al. [11]
PD-L1-positive breast cancer 12 16.6
PD-L1-negative breast cancer 124 1.6
Uncertain TNBC 59 5.2
PD-L1-positive TNBC 9 22.2
PD-L1-negative TNBC 39 2.6
Pembrolizumab PD-1 PD-L1-positive TNBC 27 18.5 Nanda et al. [19]
Uncertain TNBC 170 5.3 Adams et al. [20]
PD-L1-positive TNBC 105 5.7
PD-L1-negative TNBC 64 4.6
PD-L1-positive TNBC first line 84 21.4 Adams et al. [20]
Atezolizumab PD-L1 Uncertain TNBC 115 10.0 Emends et al. [21]
PD-L1-positive TNBC 91 11.0
PD-L1-negative TNBC 21 0.0
Uncertain TNBC first line 21 24.0
Uncertain TNBC ≥ second 94 6.0
line
ORR: Objective response rate, PD-1: Programmed cell death 1, PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1, TNBC: Triple-negative breast cancer
Table 2. Availability of immunotherapy for prevalent associated signature but are associated with significantly
cancers lower TILs . The most noticeable feature about these
[32]
subtypes is that BLIA and BLIS subtypes are, respectively,
Cancer type Availability associated with the best and the worst disease-free survival.
Bladder Immune checkpoint inhibitors, T-cell transfer therapy, To make a more vivid comparison among the subtypes, the
cancer monoclonal antibodies, treatment vaccines, and
immune system modulators [22] LAR subtype displays mutations similar to those detected in
Breast cancer Immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, luminal B cancers, and its microenvironment is described
treatment vaccines, and immune system modulators [23] as “cold,” with low TILs, in comparison with the “desert”
Cervical Immune checkpoint inhibitors, therapeutic vaccines, microenvironment in the MES subtype and the “hot”
[33]
cancer engineered T-cells, and antibody-drug conjugates [24] microenvironment in the BLIA subtype . However, it
Colorectal Immune checkpoint inhibitors and monoclonal should be noted that in these gene expression classification
cancer antibody therapies [25] systems, the vast majority of TNBCs analyzed were of
Esophageal Immune checkpoint inhibitors and monoclonal high grade; hence, it remains unclear as to how the low-
cancer antibody therapies [26] grade forms described above would fit into this taxonomy
Head and Immune checkpoint inhibitors [27] or if these low-grade forms would constitute completely
[34]
neck cancer different entities at the transcriptomic level .
Kidney cancer Interleukin-2, alpha-interferon, and immune The risk factors of TNBC are discussed below. The
checkpoint inhibitors [28] first is related to age, in which 80% of BC cases (including
Leukemia Allogeneic bone marrow transplant, therapeutic TNBCs) are older than 50 years old . Due to different sex
[6]
cancer vaccines, T-cell therapies, monoclonal antibody hormonal stimulation, female sex is considered a higher
therapies, and donor lymphocyte infusions [29]
Glioblastoma No risk for TNBC compared to male sex. In addition to these
two factors, race is also associated with TNBC, in which the
Ovarian No incidence of TNBC remains high among Caucasian non-
cancer
Hispanic women . With regard to breast tissue density,
[35]
as per clinical practice, breasts can be categorized into low-
and a high frequency of homologous recombination DNA density breasts, fatty breasts, and high-density breasts .
[36]
repair deficiency (HRD). BLIS also shows a high mutation In postmenopausal and premenopausal women, breast
rate in TP53, complex genomic profiles, and an HRD- density affects the risk of cancer, that is, the higher the
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.v1i2.196