Page 50 - TD-1-2
P. 50
Tumor Discovery Aggressive sebaceous carcinoma of the scalp
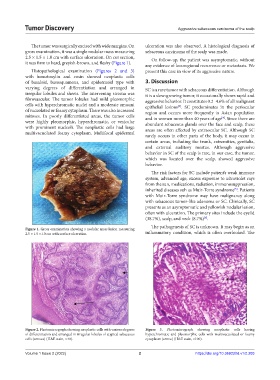
The tumor was surgically excised with wide margins. On ulceration was also observed. A histological diagnosis of
gross examination, it was a single nodular mass measuring sebaceous carcinoma of the scalp was made.
2.5 × 1.5 × 1.0 cm with surface ulceration. On cut section, On follow-up, the patient was asymptomatic, without
it was firm to hard, greyish-brown, and fleshy (Figure 1).
any evidence of locoregional recurrence or metastasis. We
Histopathological examination (Figures 2 and 3) present this case in view of its aggressive nature.
with hematoxylin and eosin showed neoplastic cells
of basaloid, basosquamous, and epidermoid type with 3. Discussion
varying degrees of differentiation and arranged in SC is a rare tumor with sebaceous differentiation. Although
irregular lobules and sheets. The intervening stroma was it is a slow-growing tumor, it occasionally shows rapid and
fibrovascular. The tumor lobules had mild pleomorphic aggressive behavior. It constitutes 0.2–4.6% of all malignant
cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and a moderate amount epithelial lesions . SC predominates in the periocular
[3]
of vacuolated or foamy cytoplasm. There was also increased region and occurs more frequently in Asian population
mitoses. In poorly differentiated areas, the tumor cells and in women more than 40 years of age . Since there are
[4]
were highly pleomorphic, hyperchromatic, or vesicular abundant sebaceous glands over the face and scalp, these
with prominent nucleoli. The neoplastic cells had large areas are often affected by extraocular SC. Although SC
multivacuolated foamy cytoplasm. Multifocal epidermal
rarely occurs in other parts of the body, it may occur in
certain areas, including the trunk, extremities, genitalia,
and external auditory meatus. Although aggressive
behavior in SC of the scalp is rare, in our case, the tumor,
which was located over the scalp, showed aggressive
behavior.
The risk factors for SC include patient’s weak immune
system, advanced age, excess exposure to ultraviolet rays
from the sun, medications, radiation, immunosuppression,
inherited diseases suh as Muir-Torre syndrome . Patients
[5]
with Muir-Torre syndrome may have malignancy along
with sebaceous tumor-like adenoma or SC. Clinically, SC
presents as an asymptomatic and yellowish nodular lesion,
often with ulceration. The primary sites include the eyelid
(38.7%), scalp, and neck (8.7%) .
[6]
The pathogenesis of SC is unknown. It may begin as an
Figure 1. Gross examination showing a nodular mass lesion measuring
2.5 × 1.5 ×1.0 cm with surface ulceration. inflammatory condition, which is often overlooked. The
Figure 2. Photomicrograph showing neoplastic cells with various degrees Figure 3. Photomicrograph showing neoplastic cells having
of differentiation and arranged in irregular lobules of atypical sebaceous hyperchromatic and pleomorphic cells with multivacuolated or foamy
cells (arrows) (H&E stain, ×40). cytoplasm (arrow) (H&E stain, ×100).
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.v1i2.203