Page 18 - TD-2-1
P. 18
Tumor Discovery Cancer progression in PCOS
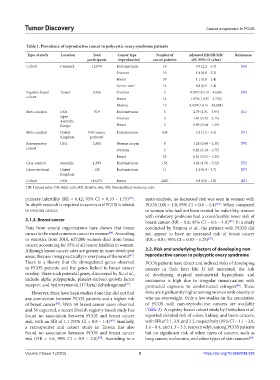
Table 1. Prevalence of reproductive cancer in polycystic ovary syndrome patients
Type of study Location Total Cancer type Number of Adjusted HR/RR/SIR/ References
participants (reproductive) cancer patients OR (95% CI value)
Cohort Denmark 12,070 Endometrium 16 3.9 (2.2 – 6.3) [69]
Ovarian 10 1.8 (0.8 – 3.2)
Breast 59 1.1 (0.8 – 1.4)
Cervix uteri 14 0.8 (0.5 – 1.4)
Registry-based Taiwan 3,566 Ovarian 2 0.997 (0.214 – 4.636) [70]
cohort Breast 14 1.976 (1.035 – 3.722)
Uterine 15 8.420 (1.615 – 43.888)
Meta-analysis USA 919 Endometrium 5 2.79 (1.31 – 5.95) [61]
Japan Ovarian 3 1.41 (0.93 – 2.15)
Australia
Europe Breast 3 0.95 (0.64 – 1.39)
Meta-analysis United 938 (cancer Endometrium 938 2.9 (1.5 – 5.5) [71]
Kingdom patients)
Retrospective USA 2,560 Uterine corpus 5 1.28 (0.49 – 3.35) [79]
cohort Ovarian 2 0.42 (0.10 – 1.75)
Breast 23 0.81 (0.53 – 1.25)
Case-control Australia 1,399 Endometrium 156 3.64 (1.76 – 7.52) [72]
Cross-sectional United 128 Endometrium 11 1.0 (0.4 – 2.7) [67]
Kingdom
Cohort USA 116,671 Breast 2267 0.8 (0.6 – 1.0) [83]
HR: Hazard ratio; OR: Odds ratio; RR: Relative risk; SIR: Standardized incidence ratio
primary infertility (RR = 0.42; 95% CI = 0.10 – 1.75) . meta-analysis, no increased risk was seen in women with
[79]
In-depth research is required to ascertain if PCOS is related PCOS (OR = 1.0; 95% CI = 0.6 – 1.4) . When compared
[61]
to ovarian cancer. to women who had not been treated for infertility, women
with ovulatory problems had a considerably lower risk of
3.1.3. Breast cancer breast cancer (RR = 0.8; 95% CI = 0.6 – 1.0) . In a study
[83]
Data from several organizations have shown that breast conducted by Brinton et al., the patients with PCOS did
[80]
cancer is the most common cancer in women . According not appear to have an increased risk of breast cancer
to statistics from 2018, 627,000 women died from breast (RR = 0.81; 95% CI = 0.53 – 1.25) .
[79]
cancer, accounting for 15% of all cancer fatalities in women.
Although breast cancer rates are greater in more developed 3.2. Risk and underlying factors of developing non-
areas, they are rising practically in every area of the world . reproductive cancer in polycystic ovary syndrome
[61]
There is a theory that the dysregulated genes observed PCOS patients have direct and indirect risks of developing
in PCOS patients and the genes linked to breast cancer cancers in their later life. If left untreated, the risk
overlap. Three such potential genes, discovered by Xu et al., of developing atypical endometrial hyperplasia and
include alpha polypeptide, platelet-derived growth factor carcinoma is high due to irregular menstruation with
receptor, and hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase . protracted exposure to unobstructed estrogen . These
[81]
[84]
However, there have been studies done that did not find risks are significantly higher among women with obesity or
any connection between PCOS patients and a higher risk who are overweight. Only a few studies on the association
of breast cancer . With 59 breast cancer cases observed of PCOS with non-reproductive cancers are available
[82]
and 56 expected, a recent Danish registry-based study has (Table 2). A registry-based cohort study by Gottschau et al.
found no association between PCOS and breast cancer reported elevated risk of colon, kidney, and brain cancers,
risk, with an SIR of 1.1 (95% CI = 0.8 – 1.4) . Similarly, with SIR of 2.1, 3.9, and 2.2, respectively (95% CI = 1.1 – 3.8,
[69]
a retrospective and cohort study in Taiwan has also 1.4 – 8.4, and 1.3 – 3.5, respectively), among PCOS patients
found no association between PCOS and breast cancer but no significant risk of other types of cancers, such as
risk (HR = 1.6, 95% CI = 0.9 – 2.8) . According to a lung cancer, melanoma, and other types of skin cancers .
[69]
[70]
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.328