Page 10 - TD-4-1
P. 10
Tumor Discovery EpCAM-targeting cancer immunotherapies
1. Introduction positive correlation between EpCAM co-expression and
pro-neovascularization growth factors. 9
Tumor cell-surface receptors (CSR) play a vital role as
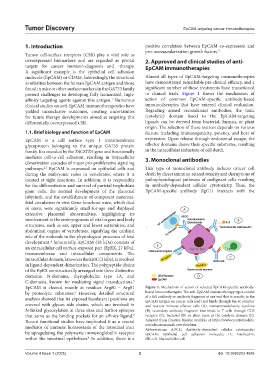
overexpressed biomarkers and are regarded as pivotal 2. Approved and clinical studies of anti-
targets for cancer immuno-diagnosis and -therapy. EpCAM immunotherapies
A significant example is the epithelial cell adhesion
molecule (EpCAM) or CD326. Interestingly, the structural Almost all types of EpCAM-targeting immunotherapies
similarities between the human EpCAM antigen and those have demonstrated remarkable pre-clinical efficacy, and a
found in mice or other surface markers in the GA733 family significant number of these treatments have transitioned
present challenges in developing fully humanized, high- to clinical trials. Figure 1 shows the mechanism of
affinity targeting agents against this antigen. Numerous action of common EpCAM-specific antibody-based
1
clinical studies on anti-EpCAM immunotherapeutics have immunotherapies that have entered clinical evaluation.
yielded inconclusive outcomes, creating uncertainties Regarding armed recombinant antibodies, the toxic
for future therapy developments aimed at targeting this (cytolytic) domain fused to the EpCAM-targeting
differentially overexpressed CSR. ligands can be derived from bacterial, human, or plant
origin. The selection of these sources depends on various
1.1. Brief biology and function of EpCAM factors, including immunogenicity, potency, and host of
EpCAM is a cell surface type 1 transmembrane expression. Upon release through endosomal escape, the
glycoprotein belonging to the unique GA733 protein effector domains cleave their specific substrates, resulting
family. It is encoded by the TACSTD1 gene and functionally in the intracellular induction of cell death.
mediates cell-to-cell adhesion, resulting in intracellular 3. Monoclonal antibodies
dimerization cascades of major pro-proliferative signaling
pathways. EpCAM is expressed on epithelial cells and This type of monoclonal antibody induces cancer cell
2,3
during the embryonic states in vertebrates, where it is death by direct immune-related toxicity and disruptions of
located at tight junctions. In addition, it is responsible pathophysiological pathways of malignant cells resulting
for the differentiation and survival of parietal trophoblast in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Thus, the
giant cells, the normal development of the placental EpCAM-specific antibody (IgG1) interacts with the
labyrinth, and the establishment of competent maternal-
fetal circulation in vivo. Gene-knockout mice, which died
in utero, were significantly small-for-age and displayed
extensive placental abnormalities, highlighting its
involvement in the embryogenesis of vital organs and body
structures, such as ear, upper and lower extremities, and
abdominal organs of vertebrates, signifying the cardinal
role of the molecule in the physiological processes of fetal
development. Structurally, EpCAM (38 kDa) consists of
4
an extracellular cell surface-exposed part (EpEX, 27 kDa),
transmembrane and intracellular components. The
intracellular domain, known as the EpIC (3 kDa), is involved
in ligand-dependent dimerization. The polypeptide chains
of the EpEX are structurally arranged into three distinctive
domains: N-domains, thyroglobulin type 1A, and
C-domains, known for mediating signal transductions.
5
EpCAM is cleaved mainly at residues Arg80 – Arg81 Figure 1. Mechanism of action of selected EpCAM-specific antibody-
by proteolytic substrates. However, detailed structural based immunotherapies. The anti-EpCAM immunotherapy types consist
6
analysis showed that its exposed basolateral positions are of a full antibody or antibody fragment at one end that is specific to the
EpCAM antigen on cancer cells (red) and binds through the Fc receptor
covered with glycan side chains, which are involved in and recruits immune effector cells (A), immunomodulatory cytokine
N-linked glycosylation at three sites and harbor epitopes (B), secondary antibody fragment that binds to T cells through CD3
that serve as the binding pockets for an affinity ligand. receptor (C), bacterial (D) or plant toxin as the cytolytic domain (E).
7
Recent functional studies have implicated it as a crucial Adapted from Creative Biolabs available at https://www.creativebiolabs.
mediator of immune homeostasis of the intestinal tract net/adecatumumab-overview.htm.
Abbreviations: ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity;
by upregulating the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; IL: Interleukin;
within the intestinal epithelium. In addition, there is a NK cell: Natural killer cell.
8
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/td.4926