Page 39 - TD-4-1
P. 39
Tumor Discovery CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in breast cancer
associated with resistance, with RB mutations detected PFS and OS compared to endocrine therapy alone. 4,8-11
through ctDNA linked to poorer PFS in patients treated The MONALEESA-2 trial exemplifies this, demonstrating
with palbociclib and fulvestrant. 27-29 Similarly, mutations prolonged PFS and improved OS when ribociclib was
in the Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog gene, added to letrozole in patients with advanced HR-positive/
detectable through ctDNA, are significantly associated HER2-negative breast cancer. 4
with resistance to palbociclib, leading to earlier tumor To address resistance, combining CDK4/6 inhibitors
relapse and reduced efficacy. In addition, upregulation of with inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mechanistic target of the
28
c-myc has been observed in palbociclib-resistant cell lines, rapamycin (mTOR) pathway has emerged as a promising
with clinical data showing that 5 – 9% of patients receiving strategy, as this pathway is frequently activated in resistant
abemaciclib developed new MYC genetic alterations tumors. mTOR inhibitors, such as everolimus have shown
15
during treatment. 29,30 potential in restoring sensitivity to endocrine therapy when
Longitudinal ctDNA analysis has identified other co-administered with AIs. Similarly, PI3K inhibitors, such
33
acquired mutations linked to resistance, including as alpelisib, combined with fulvestrant, have demonstrated
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic prolonged PFS in patients with PIK3CA-mutated advanced
subunit alpha (PIK3CA) and tumor protein p53 (TP53) luminal breast cancer. 33
alterations. Impressively, rising levels of PIK3CA- Vemurafenib is a selective BRAF inhibitor that targets
31
mutated ctDNA were detected 4 – 17 months before the B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF)
imaging evidence of progression. Moreover, genomic V600E mutation, effectively suppressing tumor growth by
complexity metrics such as blood tumor mutational inhibiting the MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase
burden derived from ctDNA have been shown to predict (ERK) signaling pathway, which is hyperactivated in
early progression during combined endocrine therapy and BRAF-mutant cancers. However, resistance to vemurafenib
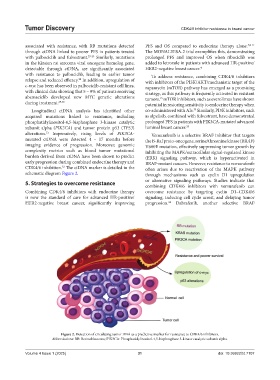
CDK4/6 inhibition. The ctDNA marker is detailed in the often arises due to reactivation of the MAPK pathway
32
schematic diagram Figure 2. through mechanisms such as cyclin D1 upregulation
5. Strategies to overcome resistance or alternative signaling pathways. Studies indicate that
combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with vemurafenib can
Combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with endocrine therapy overcome resistance by targeting cyclin D1–CDK4/6
is now the standard of care for advanced HR-positive/ signaling, inducing cell cycle arrest, and delaying tumor
HER2-negative breast cancer, significantly improving progression. Dabrafenib, another selective BRAF
34
Figure 2. Detection of circulating tumor DNA as a predictive marker for resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors.
Abbreviations: RB: Retinoblastoma; PIK3CA: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 31 doi: 10.36922/td.7107