Page 50 - TD-4-1
P. 50
Tumor Discovery WDR4 in cancer
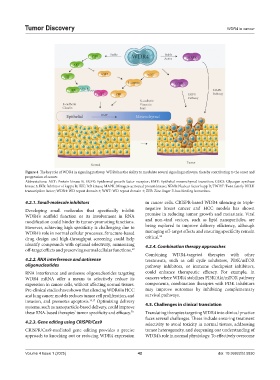
Figure 4. The key role of WDR4 in signaling pathway. WDR4 has the ability to modulate several signaling pathways, thereby contributing to the onset and
progression of cancer.
Abbreviations: AKT: Protein kinase B; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; GSK3: Glycogen synthase
kinase 3; IKB: Inhibitor of kappa B; IKK: IκB kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFκB: Nuclear factor kapp B; TWIST: Twist family BHLH
transcription factor; WDR4: WD repeat domain 4; WNT: WD repeat domain 4; ZEB: Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox.
4.2.1. Small-molecule inhibitors in cancer cells. CRISPR-based WDR4 silencing in triple-
Developing small molecules that specifically inhibit negative breast cancer and HCC models has shown
WDR4’s scaffold function or its involvement in RNA promise in reducing tumor growth and metastasis. Viral
modification could hinder its tumor-promoting functions. and non-viral vectors, such as lipid nanoparticles, are
However, achieving high specificity is challenging due to being explored to improve delivery efficiency, although
WDR4’s role in normal cellular processes. Structure-based managing off-target effects and ensuring specificity remain
drug design and high-throughput screening could help critical. 18
identify compounds with optimal selectivity, minimizing 4.2.4. Combination therapy approaches
off-target effects and preserving normal cellular functions. 69
Combining WDR4-targeted therapies with other
4.2.2. RNA interference and antisense treatments, such as cell cycle inhibitors, PI3K/mTOR
oligonucleotides pathway inhibitors, or immune checkpoint inhibitors,
RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides targeting could enhance therapeutic efficacy. For example, in
WDR4 mRNA offer a means to selectively reduce its cancers where WDR4 stabilizes PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
expression in cancer cells, without affecting normal tissues. components, combination therapies with PI3K inhibitors
Pre-clinical studies have shown that silencing WDR4 in HCC may improve outcomes by inhibiting complementary
and lung cancer models reduces tumor cell proliferation, and survival pathways.
invasion, and promotes apoptosis. 14,17 Optimizing delivery 4.3. Challenges in clinical translation
systems, such as nanoparticle-based delivery, could improve
these RNA-based therapies’ tumor specificity and efficacy. 70 Translating therapies targeting WDR4 into clinical practice
faces several challenges. These include ensuring treatment
4.2.3. Gene editing using CRISPR/Cas9 selectivity to avoid toxicity in normal tissues, addressing
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing provides a precise tumor heterogeneity, and deepening our understanding of
approach to knocking out or reducing WDR4 expression WDR4’s role in normal physiology. To effectively overcome
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 42 doi: 10.36922/td.5830