Page 52 - TD-4-2
P. 52
Tumor Discovery Role of honokiol in combination therapy
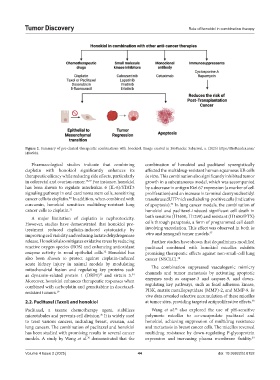
Figure 2. Summary of pre-clinical therapeutic combinations with honokiol. Image created in BioRender. Sabarwal, a. (2025) https://BioRender.com/
i48w904.
Pharmacological studies indicate that combining combination of honokiol and paclitaxel synergistically
cisplatin with honokiol significantly enhances its affected the multidrug-resistant human squamous KB cells
therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects, particularly in vitro. This combination also significantly inhibited tumor
in colorectal and ovarian cancer. 28,29 For instance, honokiol growth in a subcutaneous model, which was accompanied
has been shown to regulate interleukin 6 (IL-6)/STAT3 by a decrease in antigen Kiel 67 expression (a marker of cell
signaling pathway in oral carcinoma stem cells, sensitizing proliferation) and an increase in terminal deoxynucleotidyl
cancer cells to cisplatin. In addition, when combined with transferase dUTP nick end labeling-positive cells (indicative
30
curcumin, honokiol sensitizes multidrug-resistant lung of apoptosis). In lung cancer models, the combination of
32
cancer cells to cisplatin. 31 honokiol and paclitaxel-induced significant cell death in
A major limitation of cisplatin is nephrotoxicity. both sensitive (H1650, H1299) and resistant (H1650/PTX)
However, studies have demonstrated that honokiol pre- cells through paraptosis, a form of programmed cell death
treatment reduced cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity by involving vacuolation. This effect was observed in both in
improving cell viability and reducing lactate dehydrogenase vitro and xenograft tumor models. 37
release. Honokiol also mitigates oxidative stress by reducing Further studies have shown that dequalinium-modified
reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancing antioxidant paclitaxel combined with honokiol micelles exhibits
enzyme activity in renal epithelial cells. Honokiol has promising therapeutic effects against non-small-cell lung
32
also been shown to protect against cisplatin-induced cancer (NSCLC). 38
acute kidney injury in animal models by modulating
mitochondrial fission and regulating key proteins such The combination suppressed vasculogenic mimicry
as dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) and sirtuin 3. channels and tumor metastasis by activating apoptotic
34
33
Moreover, honokiol enhances therapeutic responses when enzymes such as caspase-3 and caspase-9, and down-
combined with carboplatin and gemcitabine in docetaxel- regulating key pathways, such as focal adhesion kinase,
resistant tumors. 19 PI3K, matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)-2, and MMP-9. In
vivo data revealed selective accumulation of these micelles
2.2. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and honokiol at tumor sites, providing targeted antiproliferative effects. 38
Paclitaxel, a taxane chemotherapy agent, stabilizes Wang et al. also explored the use of pH-sensitive
38
microtubules and prevents cell division. It is widely used polymeric micelles to co-encapsulate paclitaxel and
35
to treat various cancers, including breast, ovarian, and honokiol, achieving suppression of multidrug resistance
lung cancers. The combination of paclitaxel and honokiol and metastasis in breast cancer cells. The micelles reversed
has been studied with promising results in several cancer multidrug resistance by down-regulating P-glycoprotein
models. A study by Wang et al. demonstrated that the expression and increasing plasma membrane fluidity.
39
36
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 44 doi: 10.36922/td.8152