Page 59 - TD-4-3
P. 59
Tumor Discovery Prognostication in palliative cancer care
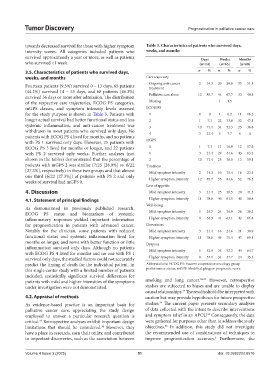
towards decreased survival for those with higher symptom Table 3. Characteristics of patients who survived days,
intensity scores. All categories included patients who weeks, and months
survived approximately a year or more, as well as patients Days Weeks Months
who survived <1 week. (n=14) (n=65) (n=68)
3.5. Characteristics of patients who survived days, n % n % n %
weeks, and months Care trajectory
Fourteen patients (9.5%) survived 0 – 13 days, 65 patients Ongoing anti-cancer 2 14.3 20 30.8 35 51.5
treatment
(44.2%) survived 14 – 55 days, and 68 patients (46.3%)
survived 56 days or more after admission. The distribution Palliative care alone 12 85.7 44 67.7 33 48.5
of the respective care trajectories, ECOG PS categories, Missing 1 1.5
mGPS classes, and symptom intensity levels assessed ECOG PS
for the study purpose is shown in Table 3. Patients with 1 0 0 4 6.2 11 16.2
longer actual survival had better functional status and less 2 1 7.1 22 33.8 32 47.1
systemic inflammation, and anti-cancer treatment was 3 10 71.4 34 52.3 25 36.8
withdrawn in most patients who survived only days. No 4 3 21.4 5 7.7 0 0
patients with ECOG PS 4 lived for months, and no patients
with PS 1 survived only days. However, 25 patients with mGPS
ECOG PS 3 lived for months or longer, and 22 patients 0 1 7.1 11 16.9 12 17.6
with PS 2 survived only weeks. Further analyses (not 1 3 21.4 29 44.6 43 63.2
shown in the tables) demonstrated that the percentage of 2 10 71.4 25 38.5 13 19.1
patients with mGPS 2 was similar (7/25 [28.0%] vs. 6/22 Tiredness
[27.3%], respectively) in these two groups and that almost Mild symptom intensity 2 14.3 10 15.4 16 23.5
one third (6/22 [27.3%]) of patients with PS 2 and only Higher symptom intensity 12 85.7 55 84.6 52 76.5
weeks of survival had mGPS 0.
Loss of appetite
4. Discussion Mild symptom intensity 3 21.4 25 38.5 28 41.2
4.1. Statement of principal findings Higher symptom intensity 11 78.6 40 61.5 40 58.8
Well-being
As demonstrated in previously published research,
ECOG PS status and biomarkers of systemic Mild symptom intensity 5 35.7 24 36.9 26 38.2
inflammatory responses yielded important information Higher symptom intensity 9 64.3 41 63.1 42 61.8
for prognostication in patients with advanced cancer. Drowsiness
Notably for the clinician, some patients with reduced Mild symptom intensity 3 21.4 16 24.6 21 30.9
functional status and systemic inflammation lived for Higher symptom intensity 11 78.6 49 75.4 47 69.1
months or longer, and some with better function or little Dyspnea
inflammation survived only days. Although no patients Mild symptom intensity 6 42.9 34 52.3 44 64.7
with ECOG PS 4 lived for months and no one with PS 1
survived only days, the studied factors could not accurately Higher symptom intensity 8 57.1 31 47.7 24 35.3
predict the timing of death for the individual patient. In Abbreviations: ECOG PS: Eastern cooperative oncology group
this single-center study with a limited number of patients performance status; mGPS: Modified glasgow prognostic score.
included, statistically significant survival differences for
patients with mild and higher intensities of the symptoms smoking and lung cancer. 34,35 However, retrospective
under investigation were not demonstrated. studies are subjected to biases and are unable to display
causal relationships. The results should be interpreted with
34
4.2. Appraisal of methods caution but may provide hypotheses for future prospective
34
As evidence-based practice is an important basis for studies. The current paper presents secondary analyses
palliative cancer care, appreciating the study design of data collected with the intent to describe interventions
33
employed to answer a particular research question is and symptom relief in an APCU. Consequently, the data
critical. Retrospective analyses exhibit important design were gathered for purposes other than to address the study
34
36
limitations that should be considered. However, they objectives. In addition, this study did not investigate
34
have a place in research, earn their utility, and contributed the recommended use of combinations of techniques to
to important discoveries, such as the association between improve prognostication accuracy. Furthermore, the
6
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 51 doi: 10.36922/td.8576