Page 95 - TD-4-3
P. 95
Tumor Discovery Sorafenib induces MVPs in NSCLC
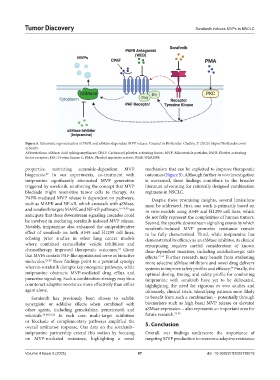
Figure 5. Schematic representation of PAFR and aSMase-dependent MVP release. Created in BioRender. Gladkiy, Y. (2025) https://BioRender.com/
a16u165.
Abbreviations: aSMase: Acid sphingomyelinase; CPAF: Carbamoyl-platelet-activating factor; MVP: Microvesicle particles; PAFR: Platelet-activating
factor-receptor; PKC: Protein kinase C; PMA: Phorbol myristate acetate; WEB: WEB2086.
properties, restricting ceramide-dependent MVP mechanism that can be exploited to improve therapeutic
biogenesis. In our experiments, co-treatment with outcomes (Figure 5). Although further in vivo investigation
27
imipramine significantly attenuated MVP generation is warranted, these findings contribute to the broader
triggered by sorafenib, reinforcing the concept that MVP literature advocating for rationally designed combination
blockade might resensitize tumor cells to therapy. As regimens in NSCLC.
PAFR-mediated MVP release is dependent on pathways, Despite these promising insights, several limitations
such as MAPK and NF-κB, which crosstalk with aSMase, must be addressed. First, our work is primarily based on
and sorafenib targets MAPK and NF-κB pathways, 16-19,50 we in vitro models using A549 and H1299 cell lines, which
anticipate that these downstream signaling cascades could do not fully represent the complexities of human tumors.
be involved in mediating sorafenib-induced MVP release. Second, the specific downstream signaling events by which
Notably, imipramine also enhanced the antiproliferative sorafenib-induced MVP promotes resistance remain
effect of sorafenib on both A549 and H1299 cell lines, to be fully characterized. Third, while imipramine has
echoing prior studies in other lung cancer models demonstrated its efficacy as an aSMase inhibitor, its clinical
where combined extracellular vesicle inhibition and repurposing requires careful consideration of known
chemotherapy improved therapeutic outcomes. Given dose-dependent toxicities, including anticholinergic side
32
that MVPs contain PAF-like agonists and serve as bioactive effects. 27,53 Further research may benefit from evaluating
molecules, 18-22 these findings point to a potential synergy more selective aSMase inhibitors and novel drug delivery
wherein sorafenib disrupts key oncogenic pathways, while systems to improve safety profiles and efficacy. Finally, the
34
imipramine obstructs MVP-mediated drug efflux and optimal dosing, timing, and safety profile for combining
paracrine signaling. Such a combination strategy may thus imipramine with sorafenib have yet to be delineated,
counteract adaptive resistance more effectively than either highlighting the need for rigorous in vivo studies and
agent alone. ultimately, clinical trials. Identifying patients most likely
Sorafenib has previously been shown to exhibit to benefit from such a combination – potentially through
synergistic or additive effects when combined with biomarkers such as high basal MVP release or elevated
other agents, including gemcitabine, pemetrexed, and aSMase expression – also represents an important area for
erlotinib. 38-40,51,52 In each case, multi-target inhibition future research. 54,55
or blockade of complementary pathways amplified the
overall antitumor response. Our data on the sorafenib– 5. Conclusion
imipramine partnership extend this notion by focusing Overall, our findings underscore the importance of
on MVP-mediated resistance, highlighting a novel targeting MVP production to overcome adaptive resistance
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 87 doi: 10.36922/TD025110019