Page 47 - AIH-2-3
P. 47
Artificial Intelligence in Health Omnichain FL in healthcare AI
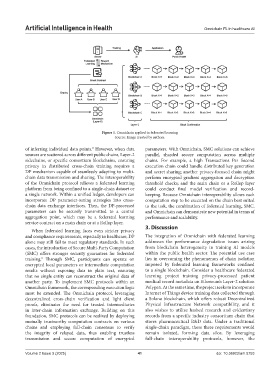
Figure 1. Omnichain applied in federated learning
Source: Image created by authors.
of inferring individual data points. However, when data parameters. With Omnichain, SMC solutions can achieve
8
sources are scattered across different public chains, Layer-2 parallel, sharded secure computation across multiple
sidechains, or specific consortium blockchains, ensuring chains. For example, a high Transactions Per Second
privacy in distributed cross-chain training requires a execution chain could handle distributed key generation
DP mechanism capable of seamlessly adapting to multi- and secret sharing; another privacy-focused chain might
chain data transmission and sharing. The interoperability perform encrypted gradient aggregation and decryption
of the Omnichain protocol relieves a federated learning threshold checks; and the main chain or a Rollup layer
platform from being confined to a single-chain dataset or could conduct final model verification and record-
a single network. Within a unified ledger, developers can keeping. Because Omnichain interoperability allows each
incorporate DP parameter-tuning strategies into cross- computation step to be executed on the chain best suited
chain data exchange interfaces. Then, the DP-processed to the task, the combination of federated learning, SMC,
parameters can be securely transmitted to a central and Omnichain can demonstrate new potential in terms of
aggregation point, which may be a federated learning performance and scalability.
service contract on a main chain or at a Rollup layer.
3. Discussion
When federated learning faces even stricter privacy
and compliance requirements, especially in healthcare, DP The integration of Omnichain with federated learning
alone may still fail to meet regulatory standards. In such addresses the performance degradation issues arising
cases, the introduction of Secure Multi-Party Computation from blockchain heterogeneity in training AI models
(SMC) offers stronger security guarantees for federated within the public health sector. The potential use case
training. Through SMC, participants can operate on lies in overcoming the phenomenon of chain isolation
9
encrypted local parameters or intermediate computation imposed by federated learning frameworks confined
results without exposing data in plain text, ensuring to a single blockchain. Consider a healthcare federated
that no single entity can reconstruct the original data of learning project training privacy-processed patient
another party. To implement SMC protocols within an medical record metadata on Ethereum’s Layer-2 solution
Omnichain framework, the corresponding execution logic Polygon. At the same time, the project seeks to incorporate
must be extended. The Omnichain protocol, leveraging Internet of Things device training data collected through
decentralized cross-chain verification and light client a Solana blockchain, which offers robust Decentralized
proofs, eliminates the need for trusted intermediaries Physical Infrastructure Network compatibility, and it
in inter-chain information exchange. Building on this also wishes to utilize hashed research and evidentiary
foundation, SMC protocols can be realized by deploying records from a specific industry consortium chain that
mutually trustworthy computation contracts on various stores pharmaceutical R&D data. Under a traditional
chains and employing full-chain consensus to verify single-chain paradigm, these three requirements would
the integrity of relayed data, thus enabling trustless remain isolated, forming data silos. By leveraging
transmission and secure computation of encrypted full-chain interoperability protocols, however, the
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 41 doi: 10.36922/aih.5753