Page 132 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 132
Wang, et al.
that of the pre-industrialization period, indicating a temperature until reaching an optimal threshold,
persistent warming trend. Over the past two decades, beyond which further temperature rises lead to a sharp
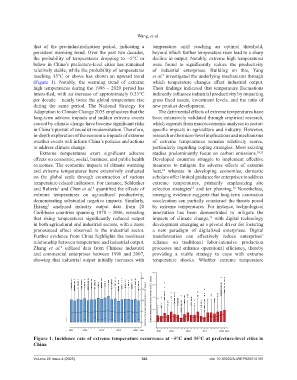
the probability of temperatures dropping to −5°C or decline in output. Notably, extreme high temperatures
below in China’s prefecture-level cities has remained were found to significantly reduce the productivity
relatively stable, while the probability of temperatures of industrial enterprises. Building on this, Yang
reaching 35°C or above has shown an upward trend et al. investigated the underlying mechanisms through
9
(Figure 1). Notably, the warming trend of extreme which temperature changes affect industrial output.
high temperatures during the 1986 – 2020 period has Their findings indicated that temperature fluctuations
intensified, with an increase of approximately 0.23°C indirectly influence industrial productivity by impacting
per decade – nearly twice the global temperature rise gross fixed assets, investment levels, and the ratio of
during the same period. The National Strategy for new product development.
Adaptation to Climate Change 2035 emphasizes that the The detrimental effects of extreme temperatures have
long-term adverse impacts and sudden extreme events been extensively validated through empirical research,
caused by climate change have become significant risks which expands from macroeconomic analyses to sector-
in China’s pursuit of socialist modernization. Therefore, specific impacts in agriculture and industry. However,
in-depth exploration of the economic impacts of extreme research on the micro-level implications and mechanisms
weather events will inform China’s policies and actions of extreme temperatures remains relatively scarce,
to address climate change. particularly regarding coping strategies. Most existing
Extreme temperatures exert significant adverse studies predominantly focus on carbon emissions. 10,11
effects on economic, social, business, and public health Developed countries struggle to implement effective
outcomes. The economic impacts of climate warming measures to mitigate the adverse effects of extreme
and extreme temperatures have extensively evaluated heat, whereas in developing economies, domestic
12
on the global scale through construction of various scholars offer limited guidance for enterprises to address
temperature-related indicators. For instance, Schlenker extreme temperatures, primarily emphasizing site
and Roberts and Chen et al. quantified the effects of selection strategies and tax planning. Nonetheless,
5
6
14
13
extreme temperatures on agricultural productivity, emerging evidence suggests that long-term innovation
demonstrating substantial negative impacts. Similarly, acceleration can partially counteract the threats posed
Hsiang analyzed industry output data from 28 by extreme temperatures. For instance, technological
7
Caribbean countries spanning 1970 – 2006, revealing innovation has been demonstrated to mitigate the
that rising temperatures significantly reduced output impacts of climate change, with digital technology
15
in both agricultural and industrial sectors, with a more development emerging as a pivotal driver for fostering
pronounced effect observed in the industrial sector. a new paradigm of digitalized enterprises. Digital
Further evidence from China highlights the nonlinear transformation can effectively reduce enterprises’
relationship between temperature and industrial output. reliance on traditional labor-intensive production
Zhang et al. utilized data from Chinese industrial processes and enhance operational efficiency, thereby
8
and commercial enterprises between 1998 and 2007, providing a viable strategy to cope with extreme
showing that industrial output initially increases with temperature shocks. Whether extreme temperature
Figure 1. Incidence rate of extreme temperature occurrence at −5°C and 35°C at prefecture-level cities in
China
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 124 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025210166