Page 135 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 135
Extreme temperature and enterprise digital transformation
3.3.2. Core explanatory variable shareholder), independent director size (Indep,
The incidence rate of extreme temperatures, including measured by the number of independent directors),
extreme high and extreme low temperatures, was Big Four audit (Big4, assigned a value of 1 if audited
measured in terms of the duration of extreme weather by one of the Big Four accounting firms, otherwise 0),
in the city, which was determined in accordance to audit opinion (Opinion, assigned a value of 1 if the
published methods. 20,34 A fixed threshold method was opinion is standard unqualified, otherwise 0), and
used, with 35°C and −5°C as the criteria: if the daily internal control index (IC, measured by the firm’s
maximum temperature exceeded 35°C, it was included internal control index); the macroeconomic control
in the number of extreme-high-temperature days, while variables include economic development level (GDP,
below −5°C, it was included in the number of extreme- measured by the natural logarithm of city GDP),
low-temperature days, which was eventually summed education level (EDU, measured by the proportion
up to obtain the specific value of the number of days of of the population with higher education in the city),
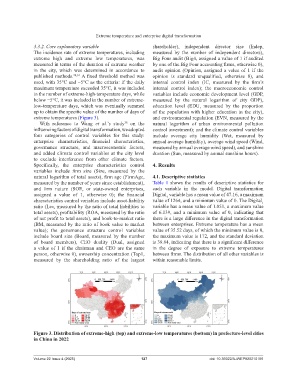
extreme temperatures (Figure 3). and environmental regulation (EVN, measured by the
With reference to Wang et al.’s study on the natural logarithm of urban environmental pollution
38
influencing factors of digital transformation, we adopted control investment); and the climate control variables
four categories of control variables for this study: include average city humidity (Wet, measured by
enterprise characteristics, financial characteristics, annual average humidity), average wind speed (Wind,
governance structure, and macroeconomic factors, measured by annual average wind speed), and sunshine
and added climate control variables at the city level duration (Sun, measured by annual sunshine hours).
to exclude interference from other climate factors.
Specifically, the enterprise characteristics control 4. Results
variables include firm size (Size, measured by the
natural logarithm of total assets), firm age (FirmAge, 4.1. Descriptive statistics
measured by the number of years since establishment), Table 1 shows the results of descriptive statistics for
and firm nature (SOE, or state-owned enterprises, each variable in the model. Digital transformation
assigned a value of 1, otherwise 0); the financial Digital variable has a mean value of 47.16, a maximum
1
characteristics control variables include asset-liability value of 1264, and a minimum value of 0. The Digital
1
ratio (Lev, measured by the ratio of total liabilities to variable has a mean value of 1.051, a maximum value
total assets), profitability (ROA, measured by the ratio of 6.139, and a minimum value of 0, indicating that
of net profit to total assets), and book-to-market ratio there is a large difference in the digital transformation
(BM, measured by the ratio of book value to market between enterprises. Extreme temperature has a mean
value); the governance structure control variables value of 35.52 days, of which the minimum value is 0,
include board size (Board, measured by the number the maximum value is 172, and the standard deviation
of board members), CEO duality (Dual, assigned is 39.64, indicating that there is a significant difference
a value of 1 if the chairman and CEO are the same in the degree of exposure to extreme temperatures
person, otherwise 0), ownership concentration (Top1, between firms. The distribution of all other variables is
measured by the shareholding ratio of the largest within reasonable limits.
Figure 3. Distribution of extreme-high (top) and extreme-low temperatures (bottom) in prefecture-level cities
in China in 2022
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 127 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025210166