Page 42 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 42
Dehdezi, et al.
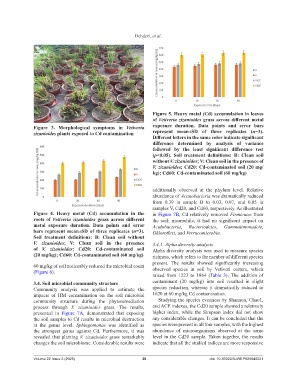
Figure 5. Heavy metal (Cd) accumulation in leaves
of Vetiveria zizanioides grass across different metal
Figure 3. Morphological symptoms in Vetiveria exposure duration. Data points and error bars
zizanioides plants exposed to Cd contamination represent mean±SD of three replicates (n=3).
Different letters in the same color indicate significant
difference determined by analysis of variance
followed by the least significant difference test
(p<0.05). Soil treatment definitions: B: Clean soil
without V. zizanioides; V: Clean soil in the presence of
V. zizanioides; Cd20: Cd-contaminated soil (20 mg/
kg); Cd60: Cd-contaminated soil (60 mg/kg)
additionally observed at the phylum level. Relative
abundance of Actinobacteria was dramatically reduced
from 0.39 in sample B to 0.03, 0.07, and 0.05 in
samples V, Cd20, and Cd60, respectively. As illustrated
Figure 4. Heavy metal (Cd) accumulation in the in Figure 7B, Cd relatively removed Firmicutes from
roots of Vetiveria zizanioides grass across different the soil; meanwhile, it had no significant impact on
metal exposure duration. Data points and error Acidobacteria, Bacteriodetes, Gammatimonadete,
bars represent mean±SD of three replicates (n=3). Ghloroflexi, and Verrucomicrobia.
Soil treatment definitions: B: Clean soil without
V. zizanioides; V: Clean soil in the presence 3.4.1. Alpha diversity analysis
of V. zizanioides; Cd20: Cd-contaminated soil Alpha diversity analysis was used to measure species
(20 mg/kg); Cd60: Cd-contaminated soil (60 mg/kg) richness, which refers to the number of different species
present. The results showed significantly increasing
60 mg/kg of soil noticeably reduced the microbial count observed species in soil by Vetiveri culture, which
(Figure 6).
raised from 1223 to 1864 (Table 3). The addition of
3.4. Soil microbial community structure contaminant (20 mg/kg) into soil resulted in slight
Community analysis was applied to estimate the species reduction, whereas it dramatically reduced to
impacts of HM contamination on the soil microbial 1620 at 60 mg/kg Cd contamination.
community structure during the phytoremediation Studying the species evenness by Shannon, Chao1,
process through V. zizanioides grass. The results, and ACE indexes, the Cd20 sample showed a relatively
presented in Figure 7A, demonstrated that exposing higher index, while the Simpson index did not show
the soil samples to Cd results in microbial destruction any considerable changes. It can be concluded that the
at the genus level. Sphingomonas was identified as species were present in all four samples, with the highest
the strongest genus against Cd. Furthermore, it was abundance of microorganisms observed at the same
revealed that planting V. zizanioides grass remarkably level in the Cd20 sample. Taken together, the results
changes the soil microbiome. Considerable results were indicate that all the studied indices are more responsive
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 36 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025040021