Page 44 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 44
Dehdezi, et al.
to microbial community evenness than to community 4. Discussion
richness.
The results indicated that Cd in the solution had a
3.4.2. Beta diversity analysis negative impact on the dry weight of V. Zizanioides
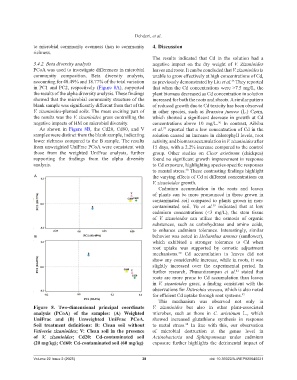
PCoA was used to investigate differences in microbial leaves and roots. It can be concluded that V. zizanioides is
community composition. Beta diversity analysis, unable to grow effectively at high concentrations of Cd,
accounting for 40.49% and 18.77% of the total variation as previously demonstrated by Liu et al. They reported
35
in PC1 and PC2, respectively (Figure 8A), supported that when the Cd concentrations were >7.5 mg/L, the
the results of the alpha diversity analysis. These findings plant biomass decreased as Cd concentration in solution
showed that the microbial community structure of the increased for both the roots and shoots. A similar pattern
blank sample was significantly different from that of the of reduced growth due to Cd toxicity has been observed
V. zizanioides-planted soils. The most exciting part of in other species, such as Brassica juncea (L.) Czem,
the results was the V. zizanioides grass controlling the which showed a significant decrease in growth at Cd
negative impacts of HM on microbial diversity. concentrations above 10 mg/L. In contrast, Aibibu
36
As shown in Figure 8B, the Cd20, Cd60, and V et al. reported that a low concentration of Cd in the
37
samples were distinct from the blank sample, indicating solution caused an increase in chlorophyll levels, root
lower richness compared to the B sample. The results activity, and biomass accumulation in V. zizanioides after
from unweighted UniFrac PCoA were consistent with 15 days, with a 2.2% increase compared to the control
those from the weighted UniFrac analysis, further group. Other studies on Cicer arietinum (chickpea)
supporting the findings from the alpha diversity found no significant growth improvement in response
analysis. to Cd exposure, highlighting species-specific responses
to mental stress. These contrasting findings highlight
38
A the varying effects of Cd at different concentrations on
V. zizanioides growth.
Cadmium accumulation in the roots and leaves
of plants can be more pronounced in those grown in
contaminated soil compared to plants grown in non-
contaminated soil. Yu et al. indicated that at low
39
cadmium concentrations (<3 mg/L), the stem tissue
of V. zizanioides can utilize the osmosis of organic
substances, such as carbohydrates and amino acids,
to enhance cadmium tolerance. Interestingly, similar
B behavior was noted in Helianthus annuus (sunflower),
which exhibited a stronger tolerance to Cd when
root uptake was supported by osmotic adjustment
mechanisms. Cd accumulation in leaves did not
40
show any considerable increase, while in roots, it was
slightly increased over the experimental period. In
further research, Phusantisampan et al. stated that
41
roots are more prone to Cd accumulation than leaves
in V. zizanioides grass, a finding consistent with the
observations for Dittrichia viscosa, which is also noted
for efficient Cd uptake through root systems. 42
This mechanism was observed not only in
Figure 8. Two-dimensional principal coordinate V. zizanioides but also in other plant-associated
analysis (PCoA) of the samples: (A) Weighted microbes, such as those in C. arietinum L., which
UniFrac and (B) Unweighted UniFrac PCoA. showed increased glutathione synthesis in response
Soil treatment definitions: B: Clean soil without to metal stress. In line with this, our observation
38
Vetiveria zizanioides; V: Clean soil in the presence of microbial destruction at the genus level in
of V. zizanioides; Cd20: Cd-contaminated soil Actinobacteria and Sphingomonas under cadmium
(20 mg/kg); Cd60: Cd-contaminated soil (60 mg/kg) exposure further highlights the detrimental impact of
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 38 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025040021