Page 18 - AN-1-1
P. 18
Advanced Neurology AIS in patients with COVID-19
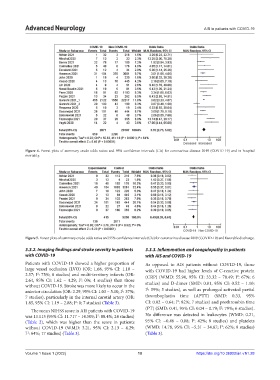
Figure 4. Forest plots of summary crude odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and in-hospital
mortality.
Figure 5. Forest plots of summary crude odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and favorable discharge.
3.3.2. Imaging findings and stroke severity in patients 3.3.3. Inflammation and coagulopathy in patients
with COVID-19 with AIS and COVID-19
Patients with COVID-19 showed a higher proportion of As opposed to AIS patients without COVID-19, those
large vessel occlusion (LVO) (OR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.10 – with COVID-19 had higher levels of C-reactive protein
2.57; I : 75%; 8 studies) and multi-territory infarcts (OR: (CRP) (WMD: 55.90, 95% CI: 33.32 – 78.49; I : 67%; 6
2
2
2.64, 95% CI: 1.62 – 4.29; I : 0%; 4 studies) than those studies) and D-dimer (SMD: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.52 – 1.10;
2
without COVID-19. Stroke was more likely to occur in the 2
anterior circulation (OR: 2.29, 95% CI: 1.03 – 5.10; I : 37%; I : 59%; 5 studies), as well as prolonged activated partial
2
7 studies), particularly in the internal carotid artery (OR: thromboplastin time (APTT) (SMD: 0.33, 95%
2
1.85, 95% CI: 1.19 – 2.88; I : 0; 7 studies) (Table 3). CI: 0.02 – 0.64; I : 82%; 7 studies) and prothrombin time
2
2
The mean NIHSS score in AIS patients with COVID-19 (PT) (SMD: 0.41, 95% CI: 0.04 – 0.79; I : 79%; 6 studies).
was 13.113 (95% CI: 11.717 – 14.509; I : 88.4%; 24 studies) No difference was detected in leukocytes (WMD: 0.21,
2
2
(Table 2), which was higher than the score in patients 95% CI: −0.46 – 0.88; I : 42%; 8 studies) and platelets
2
without COVID-19 (WMD: 3.21, 95% CI: 2.13 – 4.29; (WMD: 14.78, 95% CI: −5.31 – 34.87; I : 62%; 9 studies)
I : 64%; 17 studies) (Table 3). (Table 3).
2
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.28