Page 19 - AN-2-1
P. 19
Advanced Neurology Outcomes of implant usage for depressed skull fractures
Records identified through
database searching
Identification (n=201)
Records after duplicates removed
(n=118)
Records excluded
Screening (n=90)
- Treatment for presentations excluding
DSF
- Implant material, surgical approach
Records screened not included
(n=118) - Non-primary data (reviews,
meta-analyses)
Eligibility
Full-text articles assessed Records excluded
(n=10)
for eligibility - Implant material not described
(n=28) - DSF data insufficiently disaggregated
Included Studies included in qualitative
analysis
(n=18)
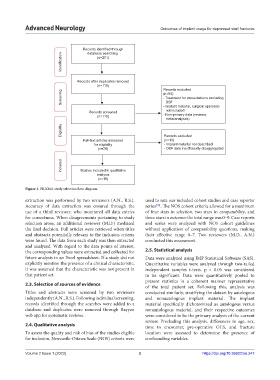
Figure 1. PRISMA study selection flow diagram.
extraction was performed by two reviewers (A.N., R.S.). used to rate our included cohort studies and case reports/
Accuracy of data extraction was ensured through the series . The NOS cohort criteria allowed for a maximum
[15]
use of a third reviewer, who monitored all data entries of four stars in selection, two stars in comparability, and
for correctness. When disagreements pertaining to study three stars in outcome: the total range was 0–9. Case reports
selection arose, an additional reviewer (M.D.) mediated and series were analyzed with NOS cohort guidelines
the final decision. Full articles were retrieved when titles without application of comparability questions, making
and abstracts potentially relevant to the inclusion criteria their effective range 0–7. Two reviewers (M.D., A.N.)
were found. The data from each study was then extracted conducted this assessment.
and analyzed. With regard to the data points of interest,
the corresponding values were extracted and collected for 2.5. Statistical analysis
future analysis in an Excel spreadsheet. If a study did not Data were analyzed using JMP Statistical Software (SAS).
explicitly mention the presence of a clinical characteristic, Quantitative variables were analyzed through two-tailed
it was assumed that the characteristic was not present in independent samples t-tests. p < 0.05 was considered
that patient set. to be significant. Data were quantitatively pooled to
present statistics in a coherent manner representative
2.3. Selection of sources of evidence
of the total patient set. Following this, analysis was
Titles and abstracts were screened by two reviewers conducted similarly, stratifying the dataset by autologous
independently (A.N., R.S.). Following individual screening, and nonautologous implant material. The implant
records identified through the searches were added to a material specifically dichotomized as autologous versus
database and duplicates were removed through Rayyan nonautologous material, and their respective outcomes
web app for systematic reviews. were considered to be the primary analysis of the current
review. Precluding this analysis, differences in age, sex,
2.4. Qualitative analysis time to encounter, pre-operative GCS, and fracture
To assess the quality and risk of bias of the studies eligible location were assessed to determine the presence of
for inclusion, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) criteria were confounding variables.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.247