Page 63 - AN-2-3
P. 63
Advanced Neurology Voluntary running effects in PTEN knockout mouse
A B J
C D
E F
G H
I
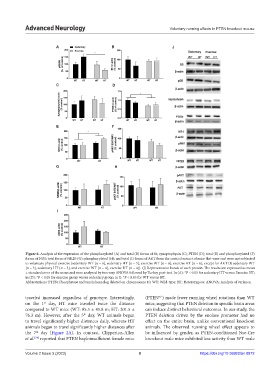
Figure 6. Analysis of the expression of the phosphorylated (A) and total (B) forms of S6; synaptophysin (C); PTEN (D); total (E) and phosphorylated (F)
forms of NR1; total form of NR2B (G); phosphorylated (H); and total (I) forms of AKT from the cortical extract of mice that were and were not subjected
to voluntary physical exercise (sedentary WT [n = 6], sedentary HT [n = 5], exercise WT [n = 6], exercise HT [n = 6], except for AKT (I) sedentary WT
[n = 5], sedentary HT [n = 5], and exercise WT [n = 4], exercise HT [n = 4]). (J) Representative bands of each protein. The results are expressed as mean
± standard error of the mean and were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Turkey post-test. In (A): *P < 0.05 for sedentary HT versus Exercise HT;
in (D): *P < 0.05 for exercise group versus sedentary group; in E: *P < 0.05 for WT versus HT.
Abbreviations: PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; WT: Wild-type; HT: Heterozygous; ANOVA: Analysis of variance.
traveled increased regardless of genotype. Interestingly, (PTEN ) made fewer running wheel rotations than WT
+/-
on the 1 day, HT mice traveled twice the distance mice, suggesting that PTEN deletion in specific brain areas
st
compared to WT mice (WT: 85.5 ± 45.8 m; HT: 201.5 ± can induce distinct behavioral outcomes. In our study, the
76.3 m). However, after the 5 day, WT animals began PTEN deletion driven by the enolase promoter had no
th
to travel significantly higher distances daily, whereas HT effect on the entire brain, unlike conventional knockout
animals began to travel significantly higher distances after animals. The observed running wheel effect appears to
the 7 day (Figure 2A). In contrast, Clipperton-Allen be influenced by gender, as PTEN-conditioned Nse-Cre
th
et al. reported that PTEN haploinsufficient female mice knockout male mice exhibited less activity than WT male
[54]
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.0872