Page 88 - AN-2-3
P. 88
Advanced Neurology Dysregulation of cAMP signaling pathway in MT2KO mice
A B C
D E F
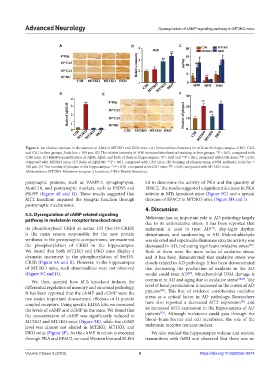
Figure 3. An obvious increase in the amount of Aβ42 in MT2KO and DKO mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry for 4G8 in the hippocampus of DG, CA3,
and CA1 in four groups. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) The relative intensity of 4G8 immunohistochemical staining in four groups. *P < 0.01, compared with
C3H mice. (C) Relative quantification of Aβ40, Aβ42, and both of them in hippocampus. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice; P < 0.01,
##
compared with MT2KO mice. (D) Ratio of Aβ42/40. **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice. (E) Staining of plaques using A3981 antibody. Scale bar =
100 μm. (F) The number of plaques in the hippocampus. **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice; P < 0.01, compared with MT2KO mice.
##
Abbreviations: MT2KO: Melatonin receptor 2 knockout; DKO: Double knockout.
presynaptic proteins, such as VAMP-2, synaptophysin, kit to determine the activity of PKA and the quantity of
MunC18, and postsynaptic markers, such as PSD93 and EPAC2. The results suggested a significant decrease in PKA
PSD95 (Figure 4F and G). These results suggested that activity in MTs knockout mice (Figure 5G) and a special
MT2 knockout impaired the synaptic function through decrease of EPAC2 in MT2KO mice (Figure 5H and I).
postsynaptic mechanisms.
4. Discussion
3.5. Dysregulation of cAMP related signaling
pathway in melatonin receptor knockout mice Melatonin has an important role in AD pathology largely
due to its antioxidative stress. It has been reported that
As phosphorylated CREB at serine 133 (Ser133-CREB) melatonin is used to treat AD , day-night rhythm
[25]
is the main reason responsible for the new protein disturbances, and sundowning in AD. Malondialdehyde
synthesis in the postsynaptic compartment, we examined was elevated and superoxide dismutase enzyme activity was
the phosphorylation of CREB in the hippocampus. decreased in AD, indicating significant oxidative stress .
[26]
We found that both MT2KO and DKO mice display a Both of them were the main index of oxidative stress,
dramatic increment in the phosphorylation of Ser133- and it has been demonstrated that oxidative stress was
CREB (Figure 5A and B). However, in the hippocampus closely related to AD pathology. It has been demonstrated
of MT1KO mice, such abnormalities were not observed that decreasing the production of oxidants in the AD
(Figure 5C and D). model could treat AD . Mitochondrial DNA damage is
[27]
We, then, queried how MTs knockout induces the common in AD and aging due to oxidative stress [28,29] . The
differential regulation of memory and neuronal pathology. level of basal peroxidation is increased in the cortex of AD
[30]
It has been reported that the cAMP and cGMP were the patients . This line of evidence corroborates oxidative
two major important downstream effectors of G-protein stress as a critical factor in AD pathology. Researchers
[31]
coupled receptors. Using specific ELISA kits, we measured have also reported a decreased MT2 expression and
the levels of cAMP and cGMP in the mice. We found that an increased MT1 expression in the hippocampus of AD
[32]
the concentration of cAMP was significantly reduced in patients . Although melatonin could pass through the
MT2KO and MT1KO mice (Figure 5E), while the cGMP blood–brain barrier and cell membrane, the role of the
level was almost not altered in MT2KO, MT1KO, and melatonin receptor remains unclear.
DKO mice (Figure 5F). As the cAMP function is executed We also studied the hippocampus volume and neuron
through PKA and EPAC2, we used Western blot and ELISA transmitters with fMRI and observed that there was no
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.0974