Page 90 - AN-2-3
P. 90
Advanced Neurology Dysregulation of cAMP signaling pathway in MT2KO mice
A B
C D
E F G
H I
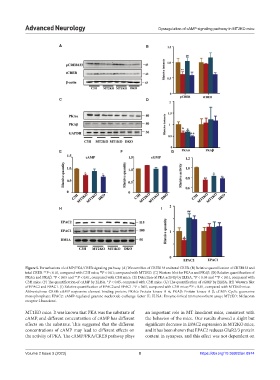
Figure 5. Perturbations of cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway. (A) Western blot of CREB133 and total CREB. (B) Relative quantification of CREB133 and
total CREB. **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice; P < 0.01; compared with MT2KO. (C) Western blot for PKAα and PKAβ. (D) Relative quantification of
##
PKAα and PKAβ. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice. (E) Detection of PKA activity by ELISA. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared with
C3H mice. (F) The quantification of cAMP by ELISA. *P < 0.05, compared with C3H mice. (G) The quantification of cGMP by ELISA. (H) Western blot
of EPAC2 and EPAC1. (I) Relative quantification of EPAC2 and EPAC1. *P < 0.05, compared with C3H mice; P < 0.01, compared with MT2KO mice.
##
Abbreviations: CREB: cAMP-responsive element binding protein; PKAα: Protein kinase A α; PKAβ: Protein kinase A β; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine
monophosphate; EPAC2: cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor II; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; MT2KO: Melatonin
receptor 2 knockout.
MT1KO mice. It was known that PKA was the substrate of an important role in MT knockout mice, consistent with
cAMP, and different concentration of cAMP has different the behavior of the mice. Our results showed a slight but
effects on the substrate. This suggested that the different significant decrease in EPAC2 expression in MT2KO mice,
concentrations of cAMP may lead to different effects on and it has been shown that EPAC2 reduces GluR2/3 protein
the activity of PKA. The cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway plays content in synapses, and this effect was not dependent on
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.0974