Page 89 - AN-2-3
P. 89
Advanced Neurology Dysregulation of cAMP signaling pathway in MT2KO mice
A B C
D E
F G
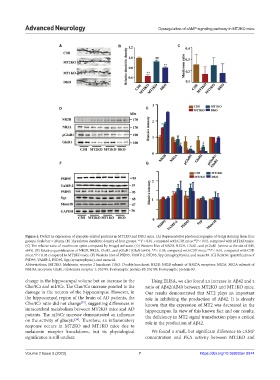
Figure 4. Deficit in expression of synaptic-related proteins in MT2KO and DKO mice. (A) Representative photomicrographs of Golgi staining from four
##
groups. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) The relative dendritic density of four groups. **P < 0.01, compared with C3H mice; P < 0.01, compared with MT2KO mice.
(C) The relative ratio of mushroom spine computed by ImageJ software. (D) Western blot of NR2B, NR2A, GluR1, and pGluR1 (serine at the site of 845,
s845). (E) Relative quantification of NR2B, NR2A, GluR1, and pGluR1 (GluR1s845). *P < 0.05, compared with C3H mice; **P < 0.01, compared with C3H
mice; P < 0.05 compared to MT2KO mice. (F) Western blot of PSD95, VAMP-2, PSD93, Syp (synaptophysin), and munc18. (G) Relative quantification of
#
PSD95, VAMP-2, PSD93, Syp (synaptophysin), and munc18.
Abbreviations: MT2KO: Melatonin receptor 2 knockout; DKO: Double knockout; NR2B: NR2B subunit of NMDA receptors; NR2A: NR2A subunit of
NMDA receptors; GluR1: Glutamate receptor 1; PSD95: Postsynaptic protein-95; PSD93: Postsynaptic protein-93.
change in the hippocampal volume but an increase in the Using ELISA, we also found an increase in Aβ42 and a
Cho/tCr and mI/tCr. The Cho/tCr increase pointed to the ratio of Aβ42/Aβ40 between MT2KO and MT1KO mice.
damage in the neuron of the hippocampus. However, in Our results demonstrated that MT2 plays an important
the hippocampal region of the brain of AD patients, the role in inhibiting the production of Aβ42. It is already
Cho/tCr ratio did not change , suggesting differences in known that the expression of MT2 was decreased in the
[33]
intracerebral metabolism between MT2KO mice and AD hippocampus. In view of this known fact and our results,
patients. The mI/tCr increase demonstrated an influence the deficiency in MT2 signal transduction plays a critical
on the activity of gliacyte . Therefore, an inflammatory role in the production of Aβ42.
[34]
response occurs in MT2KO and MT1KO mice due to
melatonin receptor knockdown, but its physiological We found a small, but significant difference in cAMP
significance is still unclear. concentration and PKA activity between MT2KO and
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.0974