Page 12 - AN-2-4
P. 12
Advanced Neurology Neonatal encephalopathy and cerebral palsy
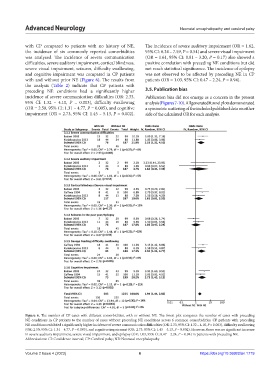
with CP compared to patients with no history of NE, The incidence of severe auditory impairment (OR = 1.62,
the incidence of six commonly reported comorbidities 95% CI: 0.34 – 7.59, P = 0.54) and severe visual impairment
was analyzed. The incidence of severe communication (OR = 1.61, 95% CI: 0.81 – 3.20, P = 0.17) also showed a
difficulties, severe auditory impairment, cortical blindness, positive correlation with preceding NE conditions but did
severe visual impairment, seizures, difficulty swallowing, not reach statistical significance. The incidence of epilepsy
and cognitive impairment was compared in CP patients was not observed to be affected by preceding NE in CP
with and without prior NE (Figure 6). The results from patients (OR = 1.03, 95% CI: 0.47 – 2.24, P = 0.94).
the analysis (Table 2) indicate that CP patients with
preceding NE conditions had a significantly higher 3.5. Publication bias
incidence of severe communication difficulties (OR: 2.33, Publication bias did not emerge as a concern in the present
95% CI: 1.32 – 4.10, P = 0.003), difficulty swallowing analysis (Figures 7-10). All generated funnel plots demonstrated
(OR = 2.50, 95% CI: 1.31 – 4.77, P = 0.005), and cognitive a symmetric scattering of the included published data on either
impairment (OR = 2.73, 95% CI: 1.45 – 5.13, P = 0.002). side of the calculated OR for each analysis.
Figure 6. The number of CP cases with different comorbidities, with or without NE. The forest plot compares the number of cases with preceding
NE conditions in CP patients to the number of cases without preceding NE conditions across 6 common comorbidities. CP patients with preceding
NE conditions exhibited a significantly higher incidence of severe communication difficulties (OR: 2.33, 95% CI: 1.32 – 4.10, P = 0.003), difficulty swallowing
(OR: 2.50, 95% CI: 1.31 – 4.77, P = 0.005), and cognitive impairment (OR: 2.73, 95% CI: 1.45 – 5.13, P = 0.002). However, there was no significant increase
in severe auditory impairment, severe visual impairment, and epilepsy (OR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.47 – 2.24, P = 0.94) in patients with preceding NE.
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; CP: Cerebral palsy; NE: Neonatal encephalopathy.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1719