Page 100 - AN-3-1
P. 100
Advanced Neurology Neurological adverse events post-vaccination
A B
C
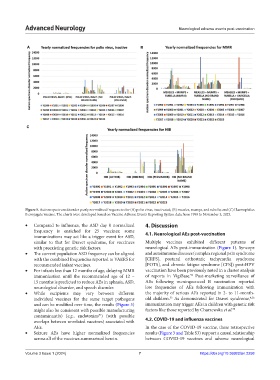
Figure 5. Autism spectrum disorder yearly normalized frequencies for (A) polio virus, inactivated; (B) measles, mumps, and rubella; and (C) Haemophilus
B conjugate vaccine. The charts were developed based on Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System data from 1990 to November 3, 2023.
• Compared to influenza, the ASD day 0 normalized 4. Discussion
frequency is enriched for 25 vaccines; some 4.1. Neurological AEs post-vaccination
immunizations may act like a trigger event for ASD,
similar to that for Dravet syndrome, for vaccinees Multiple vaccines exhibited different patterns of
with preexisting genetic risk factors. neurological AEs post-immunization (Figure 1). Syncope
• The current population ASD frequency can be aligned and autoimmune diseases (complex regional pain syndrome
with the combined frequencies reported to VAERS for [CRPS], postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
recommended infant vaccines. [POTS], and chronic fatigue syndrome [CFS]) post-HPV
• For infants less than 12 months of age, delaying MMR vaccination have been previously noted in a cluster analysis
immunization until the recommended age of 12 – of reports in VigiBase. Post-marketing surveillance of
52
15 months is predicted to reduce AEs in aphasia, ASD, AEs following meningococcal B vaccination reported
neurological disorder, and speech disorder. low frequencies of AEs following immunization with
• While excipients may vary between different the majority of serious AEs reported in 2- to 11-month-
53
individual vaccines for the same target pathogens old children. As demonstrated for Dravet syndrome,
4,36
and can be modified over time, the results (Figure 5) immunization may trigger AEs in children with genetic risk
might also be consistent with possible manufacturing factors like those reported by Charzewska et al. 38
contaminant(s) (e.g., endotoxins ) (with possible
51
overlaps between unrelated vaccines) associated with 4.2. COVID-19 and influenza vaccines
AEs. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccine, these retrospective
• Seizure AEs have higher normalized frequencies results (Figure 3 and Table S3) support a causal relationship
across all of the vaccines summarized herein. between COVID-19 vaccines and adverse neurological
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2258