Page 98 - AN-3-1
P. 98
Advanced Neurology Neurological adverse events post-vaccination
Figure 3. COVID-19 neurological adverse events by age per 100,000
vaccinations with symptoms.
higher for aphasia, ASD, and speech disorder (also higher
for HEP vaccine) (Table 1).
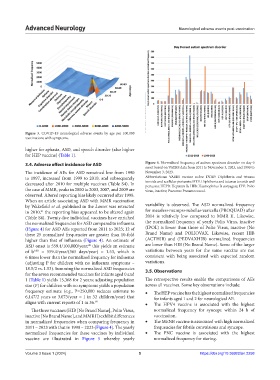
3.4. Adverse effect incidence for ASD Figure 4. Normalized frequency of autism spectrum disorder on day 0
onset based on VAERS data from 2011 to November 3, 2023, and 1990 to
The incidence of AEs for ASD remained low from 1990 November 3, 2023.
to 1997, increased from 1999 to 2010, and subsequently Abbreviations: VAERS vaccine codes: DTAP: Diphtheria and tetanus
decreased after 2010 for multiple vaccines (Table S4). In toxoids and acellular pertussis; DTP: Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and
pertussis; HEPB: Hepatitis B; HIB: Haemophilus B conjugate; IPV: Polio
the case of MMR, peaks in 2000 to 2003, 2007, and 2009 are virus, inactive; Pneumo: Pneumococcal.
observed. Altered reporting bias likely occurred after 1998.
When an article associating ASD with MMR vaccination
by Wakefield et al. published in the Lancet was retracted variability is observed. The ASD normalized frequency
in 2010, the reporting bias appeared to be altered again for measles+mumps+rubella+varicella (PROQUAD) after
21
(Table S4). Twenty-five individual vaccines have enriched 2014 is relatively low compared to MMR II. Likewise,
the normalized frequencies for ASD compared to influenza the normalized frequency of yearly Polio Virus, inactive
(Figure 4) for ASD AEs reported from 2011 to 2023; 12 of (IPOL) is lower than those of Polio Virus, inactive (No
these 25 normalized frequencies are greater than 10-fold Brand Name) and POLIOVAX. Likewise, recent HIB
higher than that of influenza (Figure 4). An estimate of (ACTHIB) and (PEDVAXHIB) normalized frequencies
ASD onset is 559.4/100,000/year; this yields an estimate are lower than HIB (No Brand Name). Some of the larger
49
of b ASD = 559.4/year/(365 days/year) = 1.53, which is variations between years for the same vaccine are not
6 times lower than the normalized frequency for influenza consistent with being associated with expected random
(adjusting P for children with no influenza symptoms – variations.
18.5/2 vs. 1.53). Summing the normalized ASD frequencies 3.5. Observations
for the seven recommended vaccines for infants aged 0 and
1 (Table 1) yields 15,368 for 2 years; adjusting population The retrospective results enable the comparisons of AEs
size (P) for children with no symptoms yields a population across all vaccines. Some key observations include:
frequency estimate (e.g., P=250,000 reduces estimate to • The HEP vaccine has the highest normalized frequencies
6,147/2 years or 3,073/year = 1 in 32 children/year) that for infants aged 1 and 2 for neurological AE.
aligns with current reports of 1 in 36. 50 • The HPV4 vaccine is associated with the highest
The three vaccines (HIB [No Brand Name], Polio Virus, normalized frequency for syncope within 24 h of
inactive [No Brand Name], and MMR II) exhibit differences vaccination.
in normalized frequencies when comparing frequency in • The MENB vaccine is associated with high normalized
2011 – 2023 with that in 1990 – 2023 (Figure 4). The yearly frequencies for febrile convulsions and syncope.
normalized frequencies for these vaccines by individual • The PNC vaccine is associated with the highest
vaccine are illustrated in Figure 5 whereby yearly normalized frequency for staring.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2258