Page 27 - AN-3-1
P. 27
Advanced Neurology BTKi in brain diseases
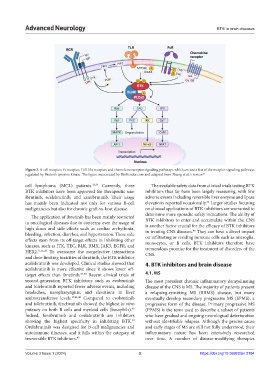
Figure 2. B-cell receptor, Fc receptor, Toll-like receptor, and chemokine receptor signaling pathways, which are just a few of the receptor signaling pathways
regulated by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. The figure was created by BioRender.com and adapted from Zhang et al.’s review. 21
cell lymphoma (MCL) patients. 33,34 Currently, three The available safety data from clinical trials testing BTK
BTK inhibitors have been approved for therapeutic use: inhibitors thus far have been largely reassuring, with few
ibrutinib, acalabrutinib, and zanubrutinib. Their usage adverse events including reversible liver enzyme and lipase
42
has mainly been indicated not only for various B-cell elevations reported occasionally. Larger studies focusing
malignancies but also for chronic graft-vs-host disease. on clinical applications of BTK inhibitors are warranted to
The application of ibrutinib has been mainly restricted determine more sporadic safety indications. The ability of
to oncological diseases due to concerns over the usage of BTK inhibitors to enter and accumulate within the CNS
is another factor crucial for the efficacy of BTK inhibitors
high doses and side effects such as cardiac arrhythmia, in treating CNS diseases. They can have a direct impact
46
bleeding, infection, diarrhea, and hypertension. These side
effects stem from its off-target effects in inhibiting other on infiltrating or residing immune cells such as microglia,
monocytes, or B cells. BTK inhibitors therefore have
kinases, such as ITK, TEC, BLK, BMX, JAK3, EGFR, and tremendous promise for the treatment of disorders of the
HER2. 11,35,36 To overcome the nonselective interactions CNS.
and dose-limiting toxicities of ibrutinib, the BTK inhibitor
acalabrutinib was developed. Clinical studies showed that 4. BTK inhibitors and brain disease
acalabrutinib is more effective since it shows lower off-
target effects than ibrutinib. 37-40 Recent clinical trials of 4.1. MS
second-generation BTK inhibitors such as evobrutinib The most prevalent chronic inflammatory demyelinating
and tolebrutinib reported fewer adverse events, including disease of the CNS is MS. The majority of patients present
headaches, nasopharyngitis, and elevations in liver a relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) disease, but many
aminotransferase levels. 17,41,42 Compared to evobrutinib eventually develop secondary progressive MS (SPMS), a
and tolebrutinib, fenebrutinib showed the highest in vitro progressive form of the disease. Primary progressive MS
potency on both B cells and myeloid cells (basophils). (PPMS) is the term used to describe a subset of patients
43
Indeed, fenebrutinib and orelabrutinib are inhibitors who have gradual and ongoing neurological deterioration
showing the highest specificity in inhibiting BTK. without identifiable relapses. Although the precise cause
44
Orelabrutinib was designed for B-cell malignancies and and early stages of MS are still not fully understood, their
autoimmune illnesses, and it falls within the category of inflammatory nature has been extensively researched
irreversible BTK inhibitors. 45 over time. A number of disease-modifying therapies
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2184