Page 38 - AN-3-1
P. 38
Advanced Neurology Antibodies as neurodegenerative biomarkers
A B
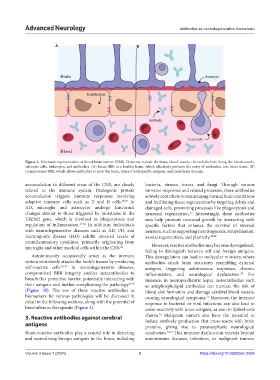
Figure 1. Schematic representation of blood-brain barrier (BBB). Elements include the brain, blood vessels, the endothelium lining the blood vessels,
astrocyte cells, leukocytes, and antibodies. (A) Intact BBB in a healthy brain, which effectively prevents the entry of antibodies into brain tissue. (B)
Compromised BBB, which allows antibodies to enter the brain, interact with specific antigens, and cause brain damage.
accumulation in different areas of the CNS, are closely bacteria, viruses, toxins, and fungi. Through various
related to the immune system. Pathogenic protein immune responses and related processes, these antibodies
accumulation triggers immune responses involving actively contribute to maintaining normal brain conditions
adaptive immune cells such as T and B cells. 38,39 In and facilitating tissue regeneration by targeting debris and
AD, microglia and astrocytes undergo functional damaged cells, promoting processes like phagocytosis and
changes similar to those triggered by mutations in the neuronal regeneration. Interestingly, these antibodies
47
TREM2 gene, which is involved in phagocytosis and may help promote neuronal growth by interacting with
regulation of inflammation. 39-41 In addition, individuals specific factors that enhance the survival of stressed
with neurodegenerative diseases such as AD, PD, and neurons, such as supporting neuritogenesis, remyelination,
Huntington’s disease (HD) exhibit elevated levels of axonal regeneration, and plasticity. 48,49
proinflammatory cytokines, primarily originating from However, reactive antibodies may become dysregulated,
microglia and other myeloid cells within the CNS. 42
failing to distinguish between self and foreign antigens.
Autoimmunity occasionally arises as the immune This dysregulation can lead to molecular mimicry, where
system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues by producing antibodies attack brain structures resembling external
self-reactive cells. 43-45 In neurodegenerative diseases, antigens, triggering autoimmune responses, chronic
compromised BBB integrity enables autoantibodies to inflammation, and neurological dysfunction. For
50
breach this protective barrier, potentially interacting with instance, in neuropsychiatric lupus, autoantibodies such
their antigens and further complicating the pathology 15,46 as antiphospholipid antibodies can increase the risk of
(Figure 1B). The use of these reactive antibodies as blood clot formation and damage cerebral blood vessels,
biomarkers for various pathologies will be discussed in causing neurological symptoms. Moreover, the immune
51
detail in the following sections, along with the potential of response to bacterial or viral infections can also lead to
biosimilars as therapeutic (Figure 2). cross-reactivity with brain antigens, as seen in Sydenham’s
52
3. Reactive antibodies against cerebral chorea. Malignant tumors also have the potential to
antigens induce antibody production that cross-reacts with brain
proteins, giving rise to paraneoplastic neurological
Brain-reactive antibodies play a crucial role in detecting syndromes. 52,53 This immune dysfunction extends beyond
and neutralizing foreign antigens in the brain, including autoimmune diseases, infections, or malignant tumors,
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2058