Page 39 - AN-3-1
P. 39
Advanced Neurology Antibodies as neurodegenerative biomarkers
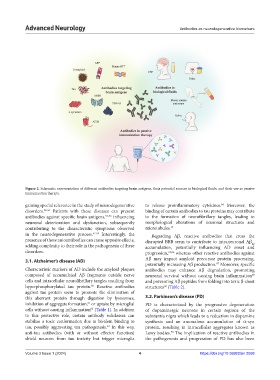
Figure 2. Schematic representation of different antibodies targeting brain antigens, their potential sources in biological fluids, and their use as passive
immunization therapy.
64
gaining special relevance in the study of neurodegenerative to release proinflammatory cytokines. Moreover, the
disorders. 54-56 Patients with these diseases can present binding of certain antibodies to tau proteins may contribute
antibodies against specific brain antigens, 54-56 influencing to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, leading to
neuronal deterioration and dysfunction, subsequently morphological alterations of neuronal structures and
contributing to the characteristic symptoms observed microtubules. 15
in the neurodegenerative process. 57-59 Interestingly, the Regarding Aβ, reactive antibodies that cross the
presence of these autoantibodies can cause opposite effects, disrupted BBB seem to contribute to intraneuronal Aβ
42
adding complexity to their role in the pathogenesis of these accumulation, potentially influencing AD onset and
disorders. progression, 65,66 whereas other reactive antibodies against
3.1. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) Aβ may impact amyloid precursor protein processing,
potentially increasing Aβ production. Moreover, specific
67
Characteristic markers of AD include the amyloid plaques antibodies may enhance Aβ degradation, promoting
composed of accumulated Aβ fragments outside nerve neuronal survival without causing brain inflammation
68
cells and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles resulting from and preventing Aβ peptides from folding into toxic β-sheet
hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Reactive antibodies structures (Table 2).
60
69
against tau protein seem to promote the elimination of
this aberrant protein through digestion by lysosomes, 3.2. Parkinson’s disease (PD)
inhibition of aggregate formation, or uptake by microglial PD is characterized by the progressive degeneration
61
cells without causing inflammation (Table 1). In addition of dopaminergic neurons in certain regions of the
62
to this protective role, certain antibody subclasses can substantia nigra which leads to a reduction in dopamine
stabilize a toxic conformation due to bivalent binding to synthesis and an anomalous accumulation of α-syn
tau, possibly aggravating tau pathogenesis. In this way, protein, resulting in intracellular aggregates known as
63
anti-tau antibodies (with or without effector function) Lewy bodies. The implication of reactive antibodies in
70
shield neurons from tau toxicity but trigger microglia the pathogenesis and progression of PD has also been
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.2058