Page 24 - AN-3-2
P. 24
Advanced Neurology Fatigue management in patients with MS
Fatigue management in PwMS
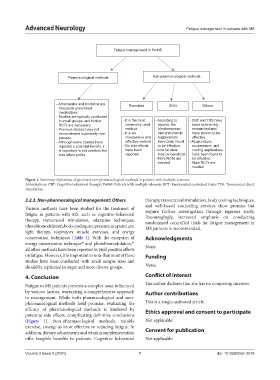
Pharmacological methods Non-pharmacological methods
- Amantadine and modafinil are Exercises Diets Others
frequently prescribed
medications
- Studies are typically conducted
in small groups, and further - It is the most - According to - CBT and TDS have
RCTs are necessary commonly used reports, the been extensively
- Previous studies have not method Mediterranean researched and
demonstrated superiority over - It is an diet and vitamin have proven to be
placebo inexpensive and supplements effective.
- Although some studies have effective method have been found - Acupuncture,
reported a potential benefit, it - No side effects to be effective. acupressure, and
is important to not overlook the have been - Low fat diets cooling applications
side effect profile reported may be beneficial have been found to
- More RCTs are be effective.
needed - More RCTs are
needed
Figure 1. Summary of pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods in patients with multiple sclerosis
Abbreviations: CBT: Cognitive behavioral therapy; PwMS: Patients with multiple sclerosis; RCT: Randomized controlled trials; TDS: Transcranial direct
stimulation.
3.2.3. Non-pharmacological management: Others therapy, transcranial stimulation, body cooling techniques,
and web-based counseling services show promise but
Various methods have been studied for the treatment of
fatigue in patients with MS, such as cognitive-behavioral require further investigation through rigorous study.
Encouragingly, increased emphasis on conducting
therapy, transcranial stimulation, relaxation techniques, randomized controlled trials for fatigue management in
photobiomodulation, body cooling, acupressure, acupuncture, MS patients is recommended.
light therapy, respiratory muscle exercises, and energy
conservation techniques (Table 4). With the exception of Acknowledgments
energy conservation technique and photobiomodulation,
81
80
all other methods have been reported to yield positive effects None.
on fatigue. However, it is important to note that most of these Funding
studies have been conducted with small sample sizes and
should be replicated in larger and more diverse groups. None.
4. Conclusion Conflict of interest
Fatigue in MS patients presents a complex issue influenced The author declares that she has no competing interests.
by various factors, warranting a comprehensive approach Author contributions
to management. While both pharmacological and non-
pharmacological methods hold promise, evaluating the This is a single-authored article.
efficacy of pharmacological methods is hindered by Ethics approval and consent to participate
potential side effects, complicating definitive conclusions
(Figure 1). Non-pharmacological methods, notably Not applicable.
exercise, emerge as most effective in reducing fatigue. In
addition, dietary adjustments and vitamin supplementation Consent for publication
offer tangible benefits to patients. Cognitive behavioral Not applicable.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/an.2576