Page 92 - AN-3-2
P. 92
Advanced Neurology Genetics of neurodevelopmental disorders in Mexico
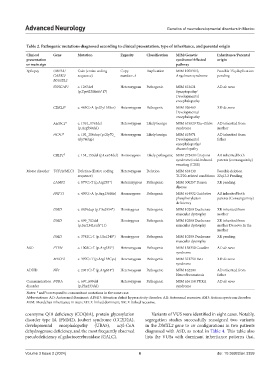
Table 2. Pathogenic mutations diagnosed according to clinical presentation, type of inheritance, and parental origin
Clinical Gene Mutation Zygosity Classification MIM/Genetic Inheritance/Parental
presentation syndrome/Affected origin
or main sign pathway
Epilepsy UBE3A/ Gain (entire coding Copy Duplication MIM 105830 S, Possible 15q duplication
GABR3/ sequence) number=4 Angelman syndrome pending
MAGEL2
SYNGAP1 c. 1267del Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 612621 AD de novo
(p.Tyr423Metfs*17) Synaptopathy/
Developmental
encephalopathy
CDKL5 θ c. 463G>A (p.Gly155Ser) Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 326463 XD de novo
Developmental
encephalopathy
AHDC1 θ c. 1761_1763del Heterozygous Likely benign MIM 615829 Xia–Gibbs AD inherited from
(p.Arg590del) syndrome mother
HCN1 δ c. 192_206dup (p.Gly70_ Heterozygous Likely benign MIM 615871 AD inherited from
Gly74dup) Developmental father
encephalopathy/
channelopathy
CRLF1 δ c. 151_153del (p.Leu51del) Homozygous Likely pathogenic MIM 272430 Crisponi AR inherited both
syndrome/cold-induced parents (consanguinity)
sweating (CISS)
Motor disorder TCF20/MLC1 Deletion (Entire coding Heterozygous Deletion MIM 618430 Possible deletion
sequence) TCF20-related conditions 22q13.2 Pending
LAMP2 c. 877C>T (p.Arg293*) Hetemizygous Pathogenic MIM 300257 Danon XR pending
disease
PNPT1 c. 407G>A (p.Arg136His) Homozygous Pathogenic MIM 614932 Oxidative AR inherited both
phosphorylation parents (Consanguinity)
deficiency
DMD c. 8859dup (p.Glu2954*) Hemizygous Pathogenic MIM 10200 Duchenne XR inherited from
muscular dystrophy mother
DMD c. 699_703del Hemizygous Pathogenic MIM 10200 Duchenne XR inherited from
(p.Ser234Leufs*11) muscular dystrophy mother De novo in the
mother
DMD c. 3742C>T (p.Gln1248*) Hemizygous Pathogenic MIM 10200 Duchenne XR pending
muscular dystrophy
ASD PTEN c. 1003C>T (p.Arg335*) Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 158350 Cowden AD de novo
syndrome
MECP2 c. 397C>T (p.Arg133Cys) Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 312750 Rett XD de novo
syndrome
ADHD NF1 c. 2041C>T (p.Arg681*) Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 162200 AD inherited from
Neurofibromatosis father
Communication PURA c. 697_699del Heterozygous Pathogenic MIM 616158 PURA AD de novo
disorder (p.Phe233del) syndrome
θ
Notes: and correspond to concomitant mutations in the same case.
δ
Abbreviations: AD: Autosomal dominant; ADHD: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; AR: Autosomal recessive; ASD: Autism spectrum disorder;
MIM: Mendelian inheritance in man; XD: X-linked dominant; XR: X-linked recessive.
coenzyme Q10 deficiency (COQ8A), protein glycosylation Variants of VUS were identified in eight cases. Notably,
disorder type IA (PMM2), Joubert syndrome (CC2D2A), segregation studies successfully reassigned two variants
developmental encephalopathy (UBA5), acyl-CoA in the DMXL2 gene to cis configurations in two patients
dehydrogenase deficiency, and the most frequently observed diagnosed with ASD, as noted in Table 4. This table also
pseudodeficiency of galactocerebrosidase (GALC). lists the VUSs with dominant inheritance patterns that,
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/an.3359