Page 96 - AN-3-2
P. 96
Advanced Neurology Genetics of neurodevelopmental disorders in Mexico
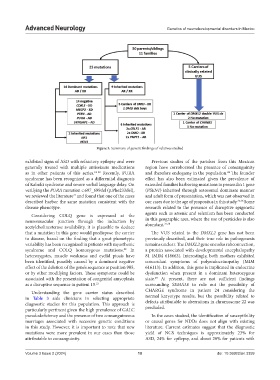
Figure 5. Summary of genetic findings of relatives studied
exhibited signs of ASD with refractory epilepsy and were Previous studies of the parishes from this Mexican
generally treated with multiple antiseizure medications region have corroborated the presence of consanguinity
as in other patients of this series. 18-20 Recently, PURA and therefore endogamy in the population. The founder
24
syndrome has been recognized as a differential diagnosis effect has also been estimated given the prevalence of
of Kabuki syndrome and severe verbal language delay. On extended families harboring mutations in presenilin 1 gene
verifying the PURA mutation c.697_699del (p.Phe233del), (PSEN1) inherited through autosomal dominant manner
we reviewed the literature and found that one of the cases and adult form of presentation, which was not observed in
21
described harbor the same mutation consistent with the our cases due to the age of propositus in this study. 25,26 Some
disease phenotype. research related to the presence of disruptive epigenetic
Considering COLQ gene is expressed at the agents such as arsenic and selenium has been conducted
neuromuscular junction through the induction by in this geographic area, where the use of pesticides is also
27,28
acetylcholinesterase availability, it is plausible to deduce abundant.
that a mutation in this gene would predispose the carrier The VUS related to the DMXL2 gene has not been
to disease, based on the finding that a great phenotypic previously described, and their true role in pathogenesis
variability has been recognized in patients with myasthenic remains unclear. The DMXL2 gene encodes rabconnection,
22
syndrome and COLQ homozygous mutations. In a protein associated with developmental encephalopathy
heterozygotes, muscle weakness and eyelid ptosis have 81 (MIM 618663). Interestingly, both mothers exhibited
been identified, possibly caused by a dominant negative concordant symptoms of polyendocrinopathy (MIM
effect of the deletion of the gene’s sequence at position 905, 616113). In addition, this gene is implicated in endocrine
or by other modifying factors. These symptoms could be dysfunction when present in a dominant heterozygous
associated with the presentation of congenital amyoplasia state. At present, there are not sufficient findings
29
as a disruptive sequence in patient 15. 23 surrounding SEMA3E to rule out the possibility of
Understanding the gene carrier status described CHARGE syndrome in patient 24 considering the
in Table 3 aids clinicians in selecting appropriate normal karyotype results, but the possibility related to
diagnostic studies for this population. This approach is defects attributable to aberrations in chromosome 22 was
particularly pertinent given the high prevalence of GALC precluded.
pseudodeficiency and the presence of two consanguineous In the cases studied, the identification of susceptibility
marriages associated with recessive genetic conditions or causal genes for NDDs does not align with existing
in this study. However, it is important to note that new literature. Current estimates suggest that the diagnostic
mutations were more prevalent in our cases than those yield of NGS techniques is approximately 23% for
attributable to consanguinity. ASD, 24% for epilepsy, and about 20% for patients with
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/an.3359