Page 11 - AN-3-4
P. 11
Advanced Neurology LBD prevalence and incidence in India
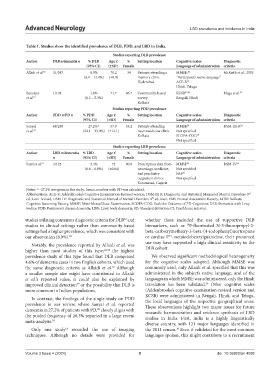
Table 1. Studies show the identified prevalence of DLB, PDD, and LBD in India.
Studies reporting DLB prevalence
Author DLB n/dementia n % DLB Age x̄ % Setting location Cognitive scales Diagnostic
(95% CI) (±SD) Female Language of administration criteria
Alladi et al. 18 31/347 8.9% 70.2 34 Patients attending a MMSE, 26 McKeith et al., 2005
(6.4 – 12.4%) (±8.0) memory clinic “Participant’s native language”
Hyderabad ACE-R 29
Hindi, Telugu
Banerjee 1/103 1.0% 71.7 46.7 Community-based KCSB 27,28 Mega et al. 23
et al. 19 (0.2 – 5.3%) survey Bengali, Hindi
Kolkata
Studies reporting PDD prevalence
Author PDD n/PD n % PDD Age x̄ % Setting location Cognitive scales Diagnostic
(95% CI) (±SD) Female Language of administration criteria
Sanyal 68/250 27.2%^ 57.9 35.2 Patients attending MMSE 26 DSM-III-R 24
et al. 20 (22.1 – 33.0%) (±12.1) neuromedicine clinic Not specified
Kolkata SCOPA-COG 30
Not specified
Studies reporting LBD prevalence
Author LBD n/dementia % LBD Age x̄ % Setting location Cognitive scales Diagnostic
n (95% CI) (±SD) Female Language of administration criteria
Patel et al. 21 3/125 2.4% 73 40.0 Prescription data from MMSE 26 DSM-IV 25
(0.8 – 6.8%) (±0.04) neurology, medicine, Not specified
and psychiatry FAB 31
outpatient clinics Not specified
Karamasad, Gujarat
Notes: ^ -27.2% was given in the study; hence, number with PD was calculated.
Abbreviations: ACE-R: Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination-Revised version, DSM-III R: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-3
rd
ed..ition–revised, DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-4 ed..ition, FAB: Frontal Assessment Battery, KCSB: Kolkata
th
Cognitive Screening Battery, MMSE: Mini-Mental State Examination, SCOPA-COG: Scale for Outcome of PD-Cognition; DLB: Dementia with Lewy
bodies; PDD: Parkinson’s disease dementia; LBD: Lewy body dementia; SD: Standard deviation; CI: Confidence interval.
studies utilizing consensus diagnostic criteria for DLB and whether these included the use of supportive DLB
22
studies in clinical settings rather than community-based biomarkers, such as F-fluorinated N-3-fluoropropyl-2-
18
settings had a higher prevalence, which was consistent with beta-carboxymethoxy-3-beta-(4-iodophenyl)nortropane
our observation (8.9%). 18 or cardiac I -metaiodobenzylguanidine, their presumed
131
Notably, the prevalence reported by Allaidi et al. was use may have supported a high clinical sensitivity in the
higher than most studies of this type; 12,34 the highest DLB cohort.
prevalence study of this type found that DLB comprised We observed significant methodological heterogeneity
4.6% of dementia cases in two English cohorts, which used for the cognitive scales adopted. Although MMSE was
12
the same diagnostic criteria as Allaidi et al. Although commonly used, only Allaidi et al. specified that this was
a smaller sample size might have contributed to Allaidi administered in the subject’s native language, and of the
et al.’s reported value, it could also be explained by languages in which MMSE was administered, only the Hindi
26
improved clinical detection or the possibility that DLB is translation has been validated. Other cognitive scales
37
more common in Indian populations. (Addenbrooke’s cognitive examination-revised version and
KCSB) were administered in Bengali, Hindi, and Telugu,
In contrast, the findings of the single study on PDD
prevalence in our review, where Sanyal et al. reported the local languages of the respective geographical areas.
These observations highlight two major issues for future
dementia in 27.2% of patients with PD, closely aligns with research: harmonization and evidence synthesis of LBD
20
the pooled frequency of 26.3% reported in a large recent studies in India. First, India is a highly linguistically
meta-analysis. 38
diverse country, with 121 major languages identified in
Only one study recorded the use of imaging the 2011 census. Even if validated for the most common
39
18
techniques. Although no details were provided for languages spoken, this might contribute to a recruitment
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/an.4098