Page 167 - AN-3-4
P. 167
Advanced Neurology ASD treatment through acupuncture
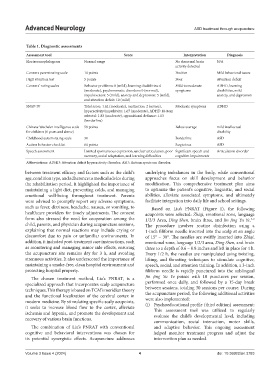
Table 1. Diagnostic assessments
Assessment tool Score Interpretation Diagnosis
Electroencephalogram Normal range No abnormal brain N/A
activity detected
Conners parent rating scale 14 points Positive Mild behavioral issues
Digit attention test 5 points Poor Attention deficit
Conners’ rating scales Behavior problems: 8 (mild), learning disabilities: 6 Mild to moderate ADHD, learning
(moderate), psychosomatic disorders: 0 (normal), symptoms disabilities, mild
impulsiveness: 5 (mild), anxiety and depression: 5 (mild), anxiety, and depression
and attention deficit: 10 (mild)
SNAP-IV Total score: 1.62 (moderate), inattention: 2 (severe), Moderate symptoms ADHD
hyperactivity/impulsivity: 1.67 (moderate), ADHD 18-item
subtotal: 1.83 (moderate), oppositional defiance: 1.13
(borderline)
Chinese Wechsler intelligence scale 58 points Below average mild intellectual
for children (6 years and above) disability
Childhood autism rating scale 30 Borderline ASD
Autism behavior checklist 64 points Suspicious ASD
Speech assessment Limited spontaneous expression, unclear articulation, poor Significant speech and Articulation disorder
memory, social adaptation, and learning difficulties cognitive impairments
Abbreviations: ADHD: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ASD: Autism spectrum disorder.
between treatment efficacy and factors such as the child’s underlying imbalances in the body, while conventional
age, condition type, and adherence to medical advice during approaches focus on skill development and behavior
the rehabilitation period. It highlighted the importance of modification. This comprehensive treatment plan aims
maintaining a light diet, preventing colds, and managing to optimize the patient’s cognitive, linguistic, and social
emotional well-being throughout treatment. Parents abilities, alleviate associated symptoms, and ultimately
were advised to promptly report any adverse symptoms, facilitate integration into daily life and school settings.
such as fever, dizziness, headache, nausea, or vomiting, to Based on Liu’s PNRAT (Figure 1), the following
healthcare providers for timely adjustments. The consent acupoints were selected: Zhiqi, emotional zone, language
form also stressed the need for cooperation among the 1/2/3 Area, Ding Shen, brain three, and Jin Jing Yu Ye.
7-9
child, parents, and physician during acupuncture sessions, The procedure involves routine disinfection using a
explaining that normal reactions may include crying or 1-inch filiform needle inserted into the scalp at an angle
discomfort due to pain or unfamiliar environments. In of 15° – 30°. The needles are swiftly inserted into Zhiqi,
addition, it included post-treatment care instructions, such emotional zone, language 1/2/3 area, Ding Shen, and brain
as monitoring and managing minor side effects, ensuring three to a depth of 0.6 – 0.8 inches and left in place for 4 h.
the acupuncture site remains dry for 3 h, and avoiding Every 1/2 h, the needles are manipulated using twisting,
strenuous activities. It also underscored the importance of lifting, and thrusting techniques to stimulate cognitive,
maintaining a smoke-free, clean hospital environment and speech, social, and attention training. In addition, a 3-inch
protecting hospital property. filiform needle is rapidly punctured into the sublingual
The chosen treatment method, Liu’s PNRAT, is a Jin Jing Yu Ye points with 10 punctures per session,
specialized approach that incorporates scalp acupuncture performed once daily, and followed by a 15-day break
techniques. This therapy is based on TCM’s meridian theory between sessions, totaling 30 sessions per course. During
and the functional localization of the cerebral cortex in the acupuncture period, the following additional activities
modern medicine. By stimulating specific scalp acupoints, were also implemented:
it seeks to increase blood flow to the cortex, alleviate (i) Psychoeducational profile (third edition) assessment:
This assessment tool was utilized to regularly
ischemia and hypoxia, and promote the development and evaluate the child’s developmental level, including
recovery of various brain functions.
communication, social interaction, motor skills,
The combination of Liu’s PNRAT with conventional and adaptive behavior. This ongoing assessment
cognitive and behavioral interventions was chosen for helped monitor treatment progress and adjust the
its potential synergistic effects. Acupuncture addresses intervention plan as needed.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/an.3783