Page 16 - AN-4-1
P. 16
Advanced Neurology Improving cognitive development in Down syndrome
Appendix
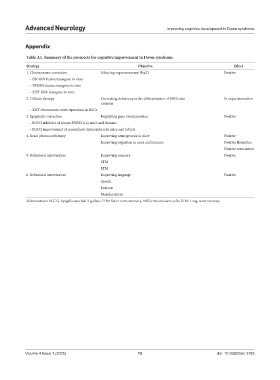
Table A1. Summary of the prospects for cognitive improvement in Down syndrome
Strategy Objective Effect
1. Chromosome correction Silencing supernumerary Hsa21 Positive
– ZSCAN4 fusion transgene in vitro
– TKNEO fusion transgene in vitro
– XIST RNA transgene in vitro
2. Cellular therapy Correcting deficiency in the differentiation of NSCs into In experimentation
neurons
– XIST chromosome-wide repression in NSCs
3. Epigenetic correction Regulating gene overexpression Positive
– EGCG inhibitor of kinase DYRK1A in mice and humans
– EGCG improvement of craniofacial dysmorphias in mice and infants
4. Brain pharmacotherapy Improving neurogenesis in mice Positive
Improving cognition in mice and humans Positive fluoxetine
Positive memantine
5. Behavioral intervention Improving memory Positive
STM
LTM
6. Behavioral intervention Improving language Positive
Speech
Lexicon
Morphosyntax
Abbreviations: EGCG: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; LTM: Short-term memory; NSCs: Neural stem cells; STM: Long-term memory.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/an.3785