Page 36 - AN-4-1
P. 36
Advanced Neurology Ferroptosis in neonatal HIBI
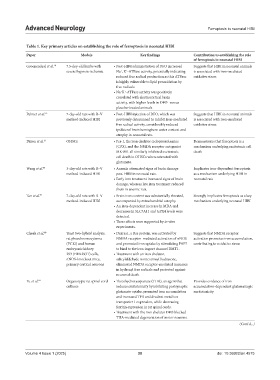
Table 1. Key primary articles on establishing the role of ferroptosis in neonatal HIBI
Paper Models Key findings Contribution to establishing the role
of ferroptosis in neonatal HIBI
Groenendaal et al. 10 7.5-day-old lambs with • Post‑HIBI administration of DFO increased Suggests that HIBI in neonatal animals
severe hypoxia-ischemia Na , K -ATPase activity, potentially indicating is associated with iron-mediated
+
+
reduced free radical production as this ATPase oxidative stress
is highly vulnerable to lipid peroxidation by
free radicals.
• Na K -ATPase activity was positively
+
+
correlated with electrocortical brain
activity, with higher levels in DFO- versus
placebo-treated animals.
Palmer et al. 13 7-day-old rats with R–V • Post‑HIBI injection of DFO, which was Suggests that HIBI in neonatal animals
method-induced HIBI previously determined to inhibit iron-mediated is associated with iron-mediated
free radical activity, considerably reduced oxidative stress
ipsilateral brain hemisphere water content and
atrophy in neonatal rats.
Dixon et al. 31 OHSCs • Fer‑1, the iron chelator ciclopiroxolamine Demonstrates that ferroptosis is a
(CPX), and the NMDA receptor antagonist mechanism underlying excitotoxic cell
MK-801 all similarly inhibited excitotoxic death
cell death in OHSCs when cotreated with
glutamate.
Wang et al. 44 3-day-old rats with R–V • Anemia attenuated signs of brain damage Implicates iron-dependent ferroptosis
method-induced HIBI post-HIBI in neonatal rats. as a mechanism underlying HIBI in
• Early iron treatment increased signs of brain neonatal rats
damage, whereas late iron treatment reduced
them in anemic rats.
Tan et al. 51 7-day-old rats with R–V • Brain iron content was substantially elevated, Strongly implicates ferroptosis as a key
method-induced HIBI accompanied by mitochondrial atrophy. mechanism underlying neonatal HIBI
• An iron‑dependent increase in MDA and
decreases in SLC7A11 and GPX4 levels were
detected.
• These effects were supported by in vitro
experiments.
Cheah et al. 68 Yeast two-hybrid analysis, • Dexras1, a Ras protein, was activated by Suggests that NMDA receptor
rat pheochromocytoma NMDA receptor–mediated activation of nNOS activation promotes iron accumulation,
(PC12) and human and promoted iron uptake by stimulating PAP7 contributing to oxidative stress
embryonic kidney to bind to the iron import channel DMT1.
293 (HEK293T) cells, • Treatment with an iron chelator,
nNOS-knockout mice, salicylaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazone,
primary cortical neurons eliminated NMDA receptor-mediated increases
in hydroxyl free radicals and protected against
neuronal death.
Yu et al. 69 Organotypic rat spinal cord • Threohydroxyaspartate (THA), an agent that Provides evidence of iron
cultures induces excitotoxicity by inhibiting postsynaptic accumulation-dependent glutamatergic
glutamate uptake, promoted iron accumulation excitotoxicity
and increased TFR and divalent metal ion
transporter 1 expression, while decreasing
ferritin expression in rat spinal cords.
• Treatment with the iron chelator DFO blocked
THA-mediated degeneration of motor neurons.
(Cont'd...)
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 30 doi: 10.36922/an.4575