Page 40 - AN-4-1
P. 40
Advanced Neurology Ferroptosis in neonatal HIBI
–
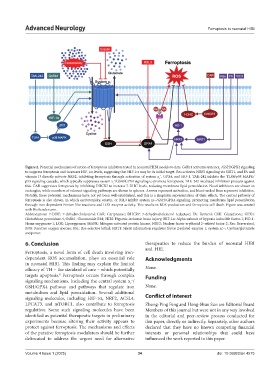
Figure 2. Potential mechanisms of action of ferroptosis inhibitors tested in neonatal HIBI models to date. GsRb1 activates system x /GSH/GPX4 signaling
c
to suppress ferroptosis and increases HIF-1α levels, suggesting that HIF-1α may be its initial target. Res activates NRF2 signaling via SIRT1, and FA and
–
vitamin D directly activate NRF2, inhibiting ferroptosis through activation of system x , GPX4, and HO-1. TAK-242 inhibits the TLR4/p38 MAPK/
c
p53 signaling cascade, which typically suppresses system x /GSH/GPX4 signaling to promote ferroptosis; TAK-242-mediated inhibition protects against
–
c
this. CAR suppresses ferroptosis by inhibiting DHCR7 to increase 7-DHC levels, reducing membrane lipid peroxidation. Novel inhibitors are shown in
rectangles, while members of relevant signaling pathways are shown in spheres. Arrows represent activation, and blunt-ended lines represent inhibition.
Notably, these potential mechanisms have not yet been well-established, and this is a simplistic representation of their effects. The central pathway of
ferroptosis is also shown, in which excitotoxicity, erastin, or RSL3 inhibit system xc–/GSH/GPX4 signaling, promoting membrane lipid peroxidation
through iron-dependent Fenton-like reactions and LOX enzyme activity. This results in ROS production and ferroptotic cell death. Figure was created
with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: 7-DHC: 7-dehydrocholesterol; CAR: Cariprazine; DHCR7: 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase; FA: Farrerol; GSH: Glutathione; GPX4:
Glutathione peroxidase-4; GsRb1: Ginsenoside Rb1; HIBI: Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury; HIF-1α: Alpha subunit of hypoxia inducible factor-1; HO-1:
Heme oxygenase-1; LOX: Lipoxygenase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NRF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; Res: Resveratrol;
ROS: Reactive oxygen species; RSL: Ras-selective lethal; SIRT1: Silent information regulator factor 2-related enzyme 1; system xc–: Cystine/glutamate
antiporter.
6. Conclusion therapeutics to reduce the burden of neonatal HIBI
and HIE.
Ferroptosis, a novel form of cell death involving iron-
dependent ROS accumulation, plays an essential role Acknowledgments
in neonatal HIBI. This finding may explain the limited
efficacy of TH – the standard of care – which potentially None.
targets apoptosis. Ferroptosis occurs through complex Funding
8
–
signaling mechanisms, including the central system x /
c
GSH/GPX4 pathway and pathways that regulate iron None.
metabolism and lipid peroxidation. Several additional
signaling molecules, including HIF-1α, NRF2, ACSL4, Conflict of interest
LPCAT3, and mTORC1, also contribute to ferroptosis Zhong-Ping Feng and Hong-Shuo Sun are Editorial Board
regulation. Some such signaling molecules have been Members of this journal but were not in any way involved
identified as potential therapeutic targets in preliminary in the editorial and peer-review process conducted for
experiments because altering their activity appears to this paper, directly or indirectly. Separately, other authors
protect against ferroptosis. The mechanisms and effects declared that they have no known competing financial
of the putative ferroptosis modulators should be further interests or personal relationships that could have
delineated to address the urgent need for alternative influenced the work reported in this paper.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 34 doi: 10.36922/an.4575