Page 87 - AN-4-3
P. 87
Advanced Neurology Exercise modulated Vitamin D and HDL in epilepsy
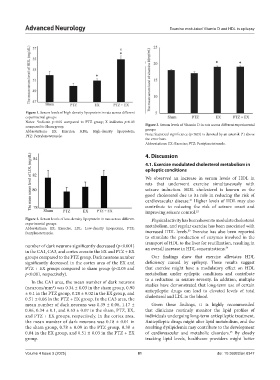
Figure 1. Serum levels of high-density lipoprotein in rats across different
experimental groups
Notes: *indicate p<0.05 compared to PTZ group; X indicates p<0.05
compared to Sham group. Figure 3. Serum levels of Vitamin D in rats across different experimental
Abbreviations: EX: Exercise; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; groups
PTZ: Pentylenetetrazole. Note: Statistical significance (p<0.05) is denoted by an asterisk (*) above
the error bars.
Abbreviations: EX: Exercise; PTZ: Pentylenetetrazole.
4. Discussion
4.1. Exercise modulated cholesterol metabolism in
epileptic conditions
We observed an increase in serum levels of HDL in
rats that underwent exercise simultaneously with
seizure induction. HDL cholesterol is known as the
good cholesterol due to its role in reducing the risk of
cardiovascular disease. Higher levels of HDL may also
21
contribute to reducing the risk of seizure onset and
improving seizure control. 22
Figure 2. Serum levels of low-density lipoprotein in rats across different Physical activity has been shown to modulate cholesterol
experimental groups metabolism, and regular exercise has been associated with
Abbreviations: EX: Exercise, LDL: Low-density lipoprotein, PTZ: 23
Pentylenetetrazole. increased HDL levels. Exercise has also been reported
to stimulate the production of enzymes involved in the
transport of HDL to the liver for reutilization, resulting in
number of dark neurons significantly decreased (p<0.001) an overall increase in HDL concentrations. 24
in the CA1, CA3, and cortex areas in the EX and PTZ + EX
groups compared to the PTZ group. Dark neurons number Our findings show that exercise alleviates HDL
significantly decreased in the cortex area of the EX and deficiency caused by epilepsy. These results suggest
PTZ + EX groups compared to sham group (p<0.05 and that exercise might have a modulatory effect on HDL
p<0.001, respectively). metabolism under epileptic conditions and contribute
to a reduction in seizure severity. In addition, multiple
In the CA1 area, the mean number of dark neurons
(neurons/mm ) was 0.34 ± 0.03 in the sham group, 0.90 studies have demonstrated that long-term use of certain
2
antiepileptic drugs can lead to elevated levels of total
± 0.1 in the PTZ group, 0.28 ± 0.02 in the EX group, and cholesterol and LDL in the blood.
0.51 ± 0.06 in the PTZ + EX group. In the CA3 area, the
mean number of dark neurons was 0.39 ± 0.06, 1.17 ± Given these findings, it is highly recommended
0.06, 0.34 ± 0.1, and 0.53 ± 0.07 in the sham, PTZ, EX, that clinicians routinely monitor the lipid profiles of
and PTZ + EX groups, respectively. In the cortex area, individuals undergoing long-term antiepileptic treatment.
the mean number of dark neurons was 0.18 ± 0.01 in Antiepileptic drugs might alter lipid metabolism, and the
the sham group, 0.78 ± 0.09 in the PTZ group, 0.38 ± resulting dyslipidemia may contribute to the development
0.04 in the EX group, and 0.51 ± 0.03 in the PTZ + EX of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. By closely
25
group. tracking lipid levels, healthcare providers might better
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 81 doi: 10.36922/an.8347