Page 68 - ARNM-1-2
P. 68
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Immunochemoradiotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma
differentiate between benign and malignant lymph nodes, effusion and diffused irregular hypertrophy in the left
further enhancing their diagnostic utility. pleura. Subsequent thoracoscopic biopsy confirmed the
diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma (epithelial
2. Case presentation type), as indicated by immunohistochemistry findings:
A 58-year-old woman who presented with dyspnea came CR(+) (Figure 1A), D2-40(+) (Figure 1B-I), Napsin A(-),
to our hospital for medical consultation and treatment. and TTF-1(-). Napsin A and TTF-1 are commonly used
A series of investigations were conducted on the patient immunohistochemical markers for the identification
to better comprehend her condition. Chest computed of lung adenocarcinoma, while D2-40 is an established
tomography (CT) revealed the presence of pleural immunohistochemical marker crucial for diagnosing
A B C J K L M
D E F
N O P Q
G H I
R S
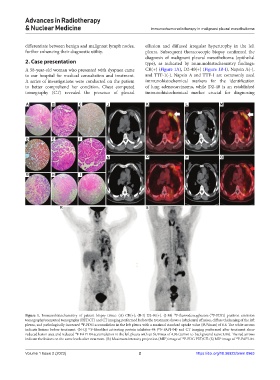
Figure 1. Immunohistochemistry of patient biopsy tissue: (A) CR(+); (B-I) D2-40(+). (J-M) F-fluorodeoxyglucose ( F-FDG) positron emission
18
18
tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) and CT imaging performed before the treatment shows a left pleural effusion, diffuse thickening of the left
pleura, and pathologically increased F-FDG accumulation in the left pleura with a maximal standard uptake value (SUVmax) of 6.6. The white arrows
18
indicate lesions before treatment. (N-Q) F-fibroblast activating protein inhibitor-04 ( F-FAPI-04) and CT imaging performed after treatment show
18
18
reduced lesion area and reduced F-FAPI-04 accumulation in the left pleura with an SUVmax of 4.96 (tumor-to-background ratio: 3.06). The red arrows
18
indicate the lesions on the same levels after treatment. (R) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) image of F-FDG PET/CT. (S) MIP image of F-FAPI-04.
18
18
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.0963